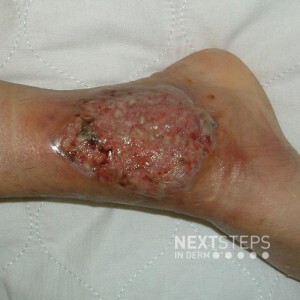
The correct answer is E. PAPA syndrome.
The image shows classic ulcerative pyoderma gangrenosum with undermined violaceous gray border. Re-epithelialization occurs from the margins and the ulcer heals usually with atrophic cribriform pigmented scar. Although the classic morphologic clinical presentation of pyoderma gangrenosum is an ulceration, there are several variants (bullous, pustular, and superficial granulomatous) which differ by their clinical presentation, location, and associated diseases.
SAPHO syndrome: SAPHO syndrome is characterized by any combination of: Synovitis (inflammation of the joints), Acne (conglobata or fulminans), Pustulosis (thick yellow blisters containing pus) often on the palms and soles and similar to palmoplantar pustular psoriasis). Follicular occlusion tetrad syndrome: Follicular occlusion syndrome refers to a group of diseases in which hair follicles become blocked with keratin (scale) and then rupture, resulting in inflammatory skin disease. These conditions commonly coexist. They may be severe and difficult to treat. This includes hidradenitis suppurativa, acne conglobata, dissecting cellulitis, and pilonidal cyst or sinuses. LEOPARD syndrome: Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines (NSML), formerly known as LEOPARD syndrome, is a very rare inherited disorder that is characterized by skin, heart, ear, genital, head and facial abnormalities. NAME syndrome: Myxoma syndrome is the name given to a group of diseases that are characterized by the presence of atrial myxomas (tumors of heart tissue) and lentigines (pigmented spots on the skin).
References:
Cugno M, Borghi A, Marzano AV. PAPA, PASH and PAPASH Syndromes: Pathophysiology, Presentation and Treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18(4):555-562. doi:10.1007/s40257-017-0265-1.
Brought to you by our Brand Partner
![]()
