The correct answer is E. Disease reactivation after reconstructive filler injection is high.
There are no reports in the literature of lupus reactivation after reconstructive injectable treatment.
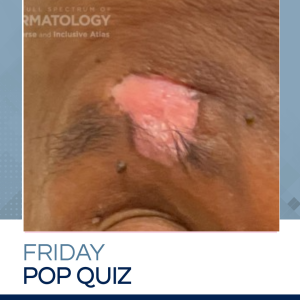
Lesions of discoid LE are characterized by dyspigmentation, telangiectasias, and atrophic, hypertrophic, cribriform, and/or acneiform scarring. Strict photoprotection and medical management with topical and systemic immunomodulatory therapies comprise the first line of treatment.
Pulsed dye laser (PDL) can be used at low fluences to treat cutaneous lupus lesions. PDL treatment may even prevent disease progression, and therefore some authors advocate for early use of PDL. DLE scarring has also been reported to respond to erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser.
Several studies have shown success with the use of injectables in correcting atropic cutaneous lupus lesions. There are no reports in the literature of lupus reactivation after reconstructive injectable treatment. Fat transfer has the highest level of evidence, and should be performed only when patient is off immunosuppressive medications and disease is inactive. Avoid HA fillers as cases of delayed onset, immune mediated nodules have been reported.
References: Creadore A, Watchmaker J, Maymone MBC, Pappas L, Vashi NA, Lam C. Cosmetic treatment in patients with autoimmune connective tissue diseases: Best practices for patients with lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Aug;83(2):343-363. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.123. Epub 2020 Apr 28. PMID: 32360722.
