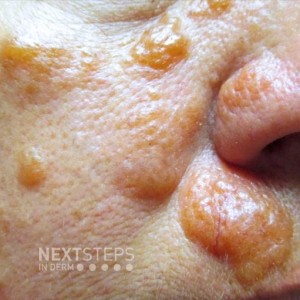
The correct answer is D. Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma.
The patient has necrobiotic xanthogranuloma (NXG) associated with a monoclonal gammopathy, which is most often an IgG kappa or lambda monoclonal gammopathy. NXG is a rare, chronic, progressive granulomatous disorder. It manifests as yellowish plaques and nodules most commonly in the mid face to periocular region.
Sarcoidosis presents more commonly as pink predominant papules with a yellow tinge on the nose and nasal columella and is not classically associated with a monoclonal gammopathy. Leprosy is an infectious cause of leonine facies but is not associated with pink granulomatous plaques on the face with an associated monoclonal gammopathy. Phymatous rosacea presents on the nose to medial cheeks with sebaceous gland hyperplasia leading to lobular and sebaceous, disfiguring appearance to the nose. Cutaneous tuberculosis is not associated with monoclonal gammopathy.
References: Girisha BS, Holla AP, Fernandes M, Noronha TM. Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2012;5(1):43–45. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.94341
Brought to you by our Brand Partner
![]()
