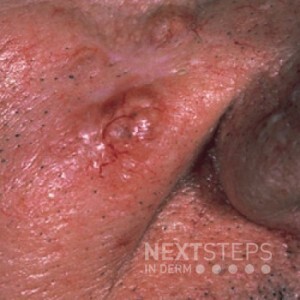
The correct answer is D. Gorlin Syndrome.
The image shows a basal cell carcinoma. One genodermatosis associated with numerous BCCs is Gorlin syndrome/basal cell nevus syndrome. It is due to a mutation in PTCH gene. Patients with Gorlin Syndrome can display – Odontogenic keratocysts of the jaw, palmoplantar pits, calcification of the falx cerebri, and skeletal abnormalities. In addition to BCCs, patients have an increased risk for medulloblastomas, meningiomas, ovarian fibromas, and cardiac fibromas. BCCs usually begin to appear in the late teens to early 20s and favor sun exposed sites. Treatment is aimed at prevention strategies, many advocate for less aggressive surgical approaches to patients and using surgical techniques (ex: mohs) for aggressive tumor types. Additionally, hedgehog inhibitors are deployed to help with multiple tumors or in cases where surgical techniques would lead to high morbidity. Other syndromes with increased risk for BCC include: Bazex syndrome, Rombo syndrome, Xeroderma Pigmentosum, and others.
Cowden and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba (BRR) are due to a PTEN mutation. Cowden syndrome (multile hamaratomas) is associated with: Tricholemmomas, oral papillomas, palmoplantar keratoses, and cancers such as thyroid cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, and melanoma. BRR is associated with: multiple lipomas, lentigines of the genitals, vascular malformations, macrocephaly, mental retardation, intestinal polyps, and thyroid tumors. Birt-Hogg-Dube is due to a folliculin mutation. It is associated with: fibrofolliculomas, acrochordons, renal tumors, trichodiscomas, spontaneous pneumothorax (due to pulmonary cysts) (mneumonic: hog FARTS) Carney is due to PRKAR1A mutation. Associations with Carney complex have been called NAME and LAMB in the past for: Nevi, Atrial myxoma, Myxoid neurofibromas, and ephelides – or – Lentigines, Atrial Myxomas, and Blue nevi, respectively. Testicular cancer (Sertoli cell type), psammomatous melanotic schwannomas, and primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease are also associations.
References: In Bolognia, J., In Schaffer, J. V., & In Cerroni, L. (2018). Dermatology.
