Nivolumab Therapeutic Cheat Sheet
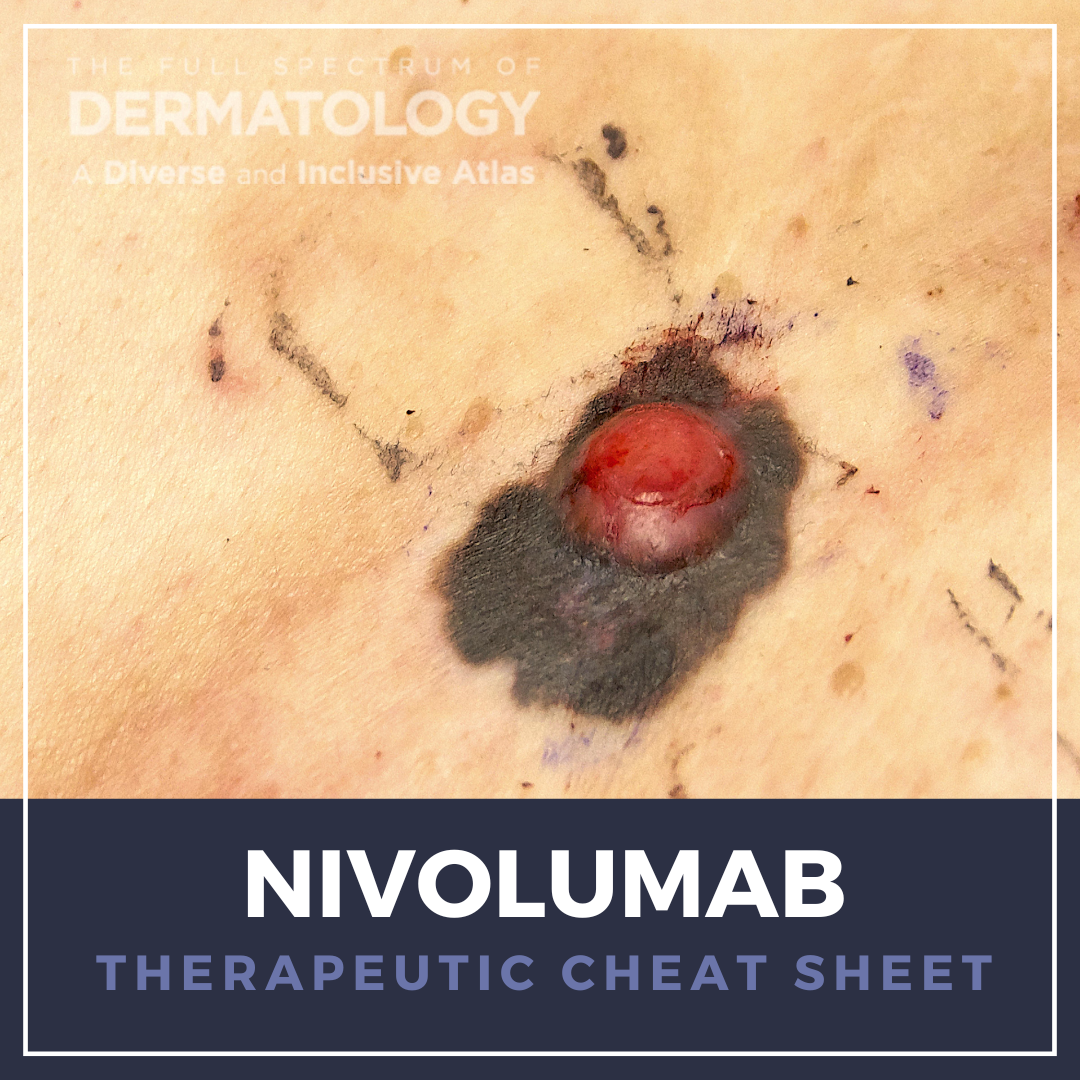 Nivolumab, a programmed death-1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitor, is a cornerstone in the evolving field of immuno-oncology. Originally developed for advanced cancers, nivolumab functions by blocking PD-1–mediated immune suppression, thereby enhancing T-cell–mediated antitumor responses. In dermatology, its relevance has grown not only because of its utility in melanoma treatment and cutaneo …
Nivolumab, a programmed death-1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitor, is a cornerstone in the evolving field of immuno-oncology. Originally developed for advanced cancers, nivolumab functions by blocking PD-1–mediated immune suppression, thereby enhancing T-cell–mediated antitumor responses. In dermatology, its relevance has grown not only because of its utility in melanoma treatment and cutaneo …
 Nivolumab, a programmed death-1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitor, is a cornerstone in the evolving field of immuno-oncology. Originally developed for advanced cancers, nivolumab functions by blocking PD-1–mediated immune suppression, thereby enhancing T-cell–mediated antitumor responses. In dermatology, its relevance has grown not only because of its utility in melanoma treatment and cutaneo …
Nivolumab, a programmed death-1 (PD-1) immune checkpoint inhibitor, is a cornerstone in the evolving field of immuno-oncology. Originally developed for advanced cancers, nivolumab functions by blocking PD-1–mediated immune suppression, thereby enhancing T-cell–mediated antitumor responses. In dermatology, its relevance has grown not only because of its utility in melanoma treatment and cutaneo … 

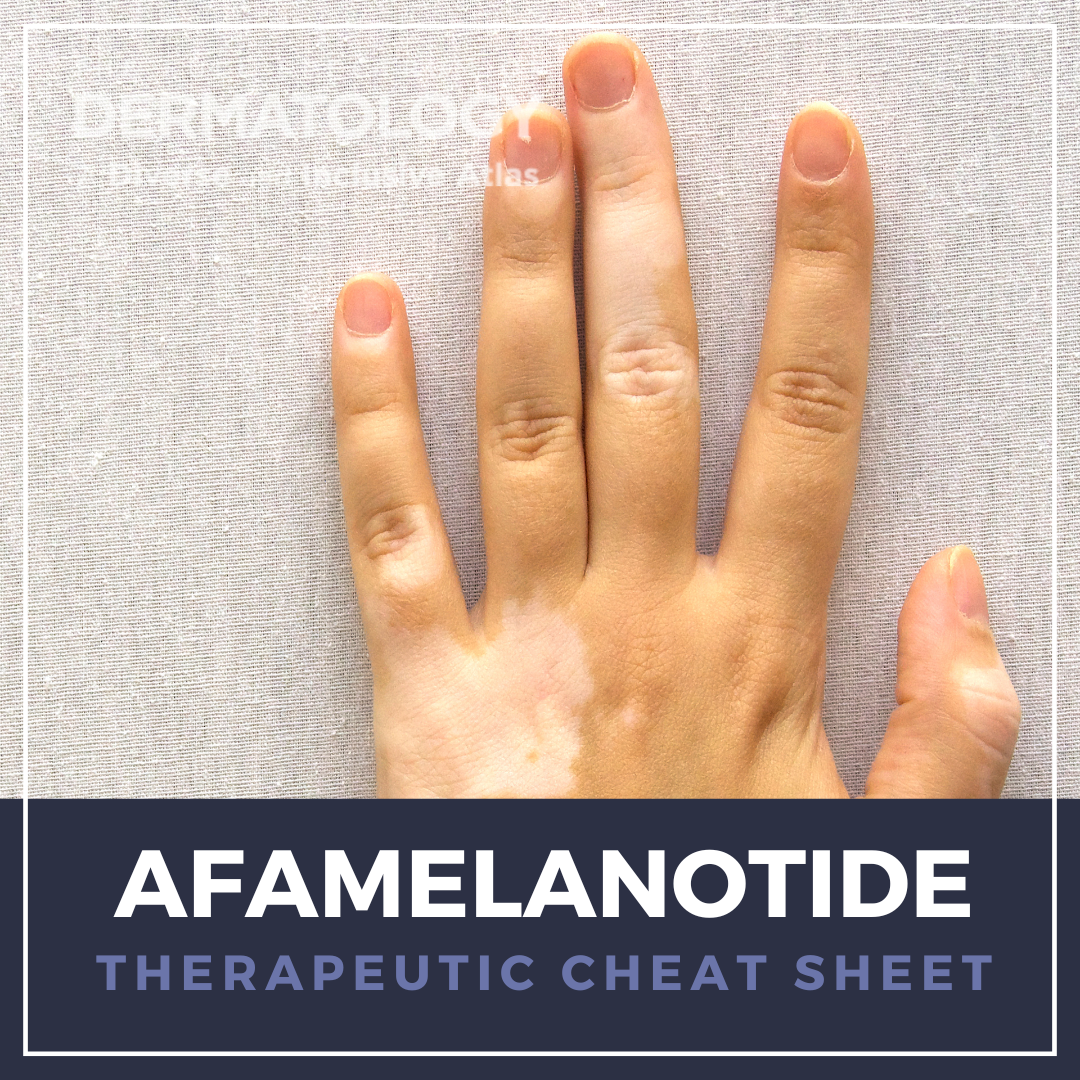 Photosensitive skin conditions can result in cutaneous and systemic symptoms that can have a marked effect on quality of life due to ubiquitous UV exposure. Erythropoietic protoporphyria, for example, can cause severe photodermatitis, excruciating burning and neuropathic pain, nausea, and deep-rooted fear of sunlight that leads to debilitating lifestyle modifications such as remaining indoors. We …
Photosensitive skin conditions can result in cutaneous and systemic symptoms that can have a marked effect on quality of life due to ubiquitous UV exposure. Erythropoietic protoporphyria, for example, can cause severe photodermatitis, excruciating burning and neuropathic pain, nausea, and deep-rooted fear of sunlight that leads to debilitating lifestyle modifications such as remaining indoors. We … 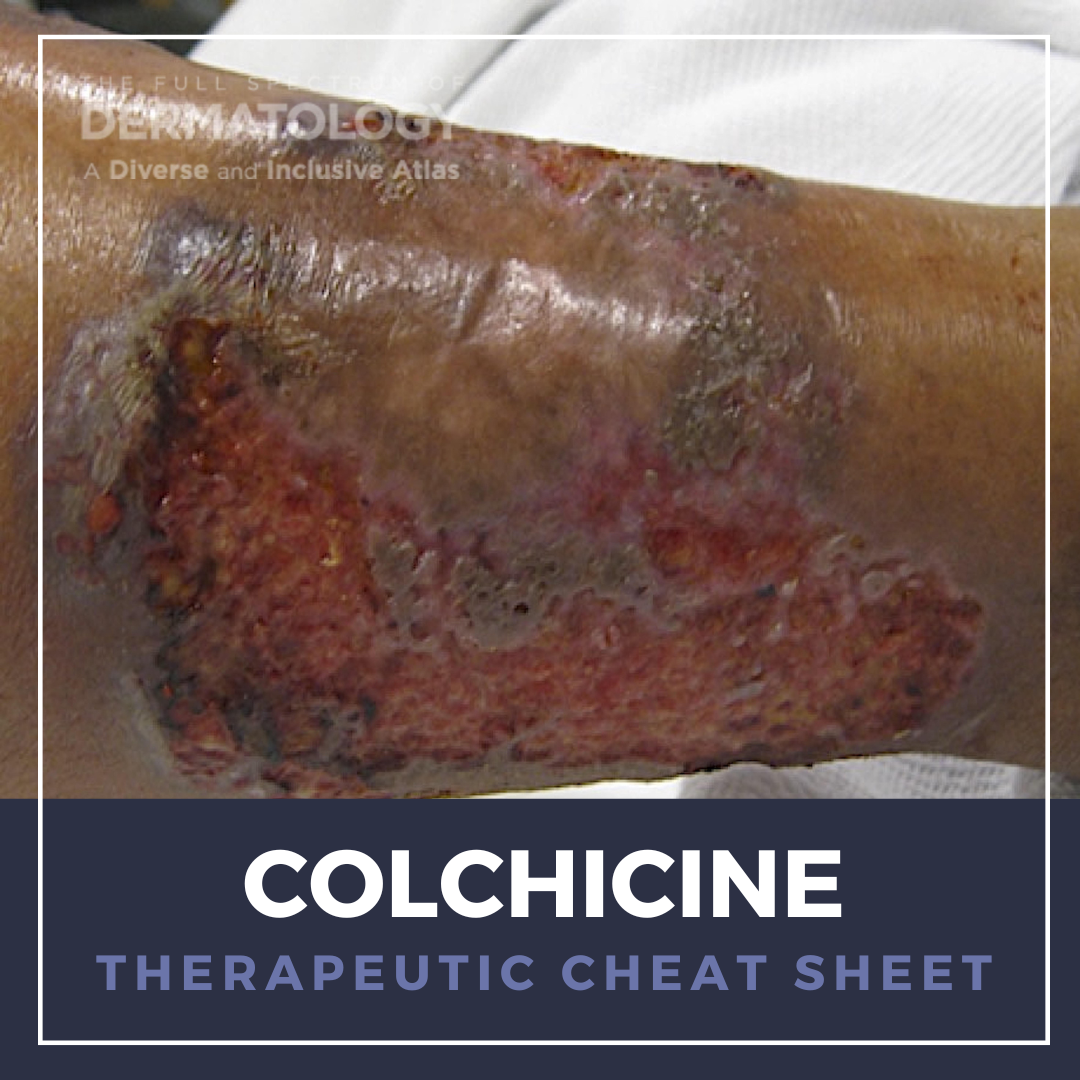 Colchicine, a microtubule polymerization inhibitor, was first described for use in treating joint pain and swelling in ancient Egypt and has since become a mainstay in the medical management of gout. Beyond its indicated uses, it has numerous off-label dermatologic applications, particularly for neutrophilic and autoimmune conditions. As a potent anti-inflammatory, colchicine requires careful lab …
Colchicine, a microtubule polymerization inhibitor, was first described for use in treating joint pain and swelling in ancient Egypt and has since become a mainstay in the medical management of gout. Beyond its indicated uses, it has numerous off-label dermatologic applications, particularly for neutrophilic and autoimmune conditions. As a potent anti-inflammatory, colchicine requires careful lab … 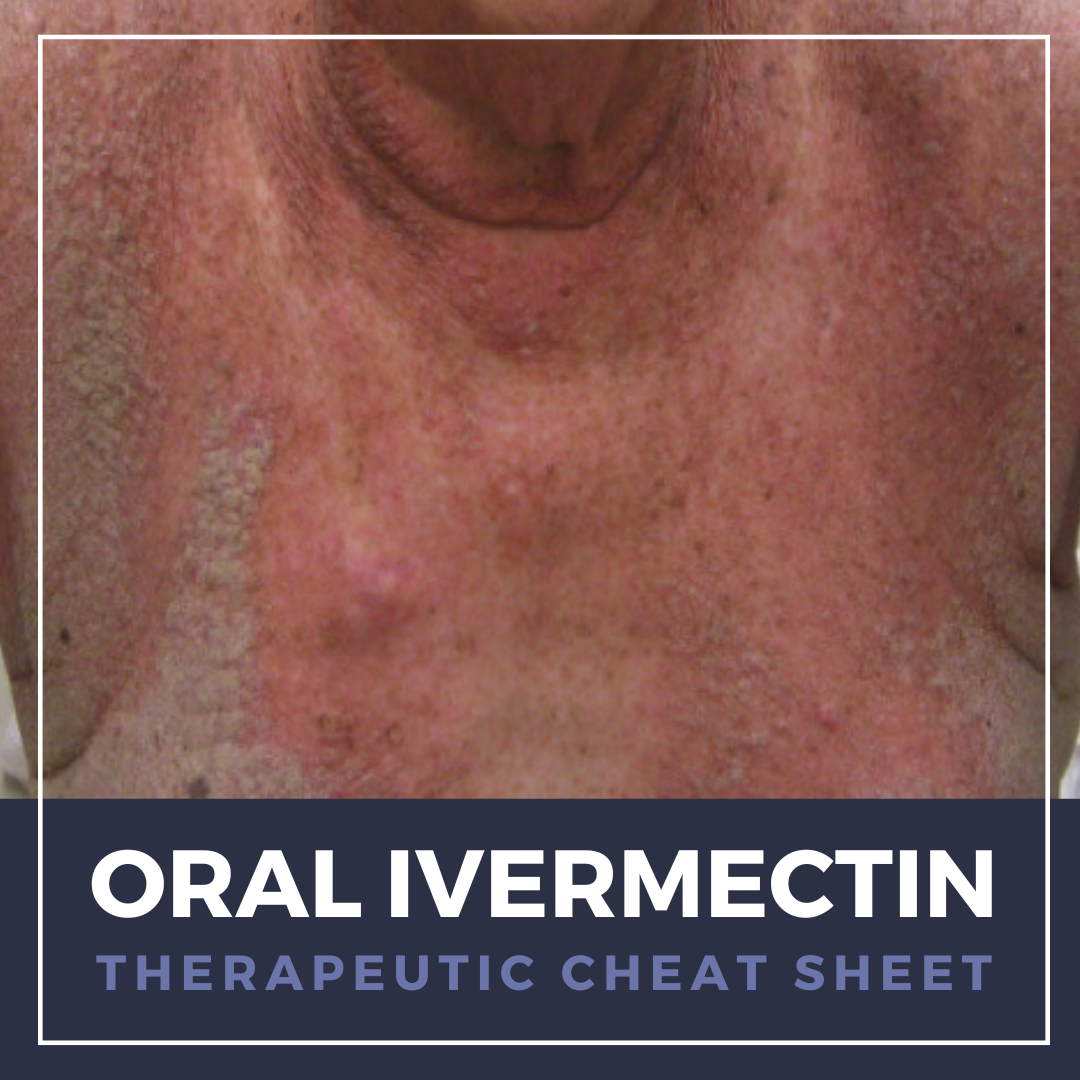 Ivermectin is a semi-synthetic derivative of avermectins, a class of macrocyclic lactones with broad-spectrum anti-parasitic effects. Its unique mechanism of action, favorable safety profile, and anti-inflammatory properties make ivermectin invaluable in the treatment of a wide range of cutaneous parasitic infestations, including scabies. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a cl …
Ivermectin is a semi-synthetic derivative of avermectins, a class of macrocyclic lactones with broad-spectrum anti-parasitic effects. Its unique mechanism of action, favorable safety profile, and anti-inflammatory properties make ivermectin invaluable in the treatment of a wide range of cutaneous parasitic infestations, including scabies. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a cl … 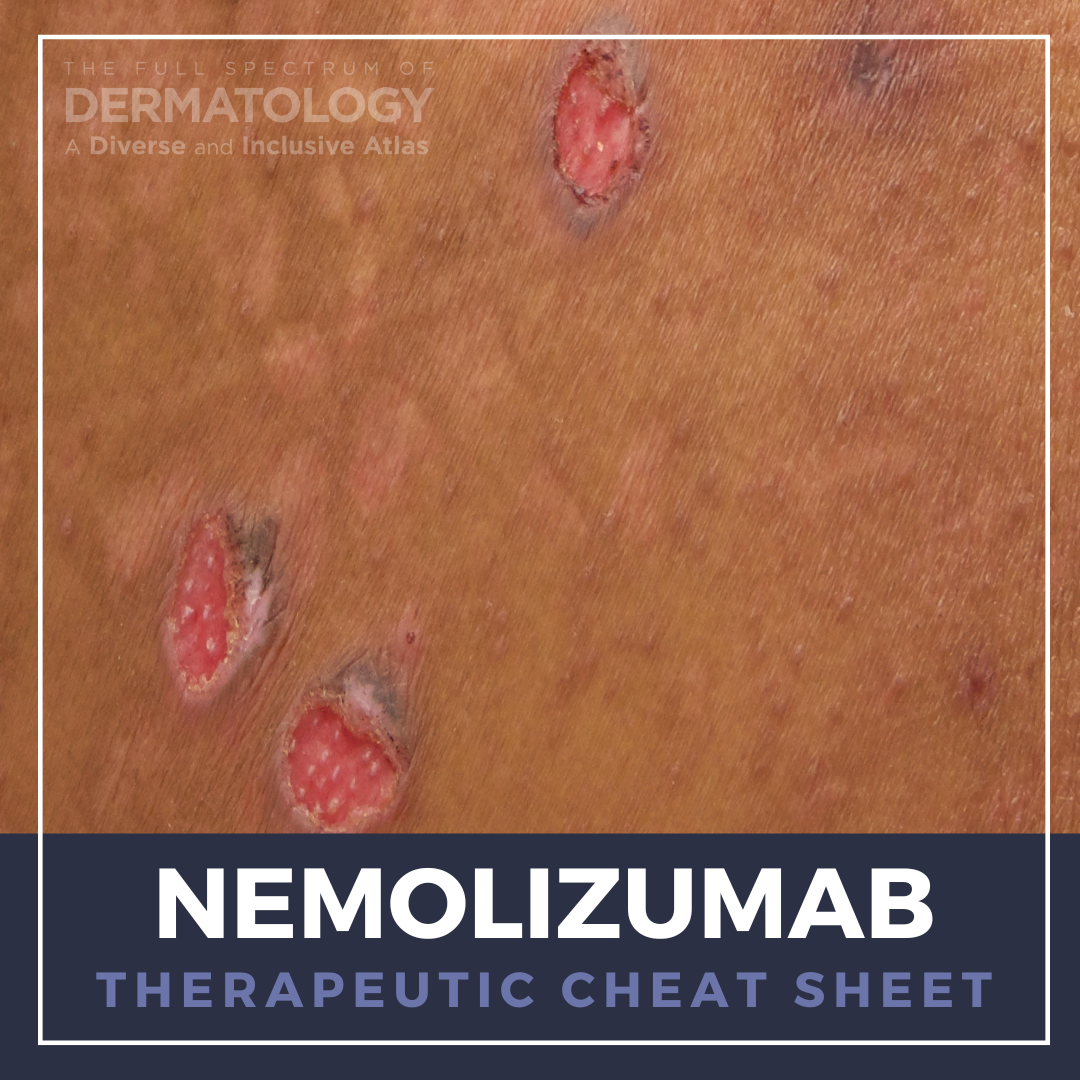 Atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis are chronic, life-altering diseases with a common feature of debilitating pruritus that significantly impacts our patients’ qualities of life. For those with resistant and extensive disease, dermatologists now have nemolizumab in our armamentarium, the first FDA approved IL-31 inhibitor. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a closer look a …
Atopic dermatitis and prurigo nodularis are chronic, life-altering diseases with a common feature of debilitating pruritus that significantly impacts our patients’ qualities of life. For those with resistant and extensive disease, dermatologists now have nemolizumab in our armamentarium, the first FDA approved IL-31 inhibitor. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a closer look a …