The correct answer is B. Wound culture.
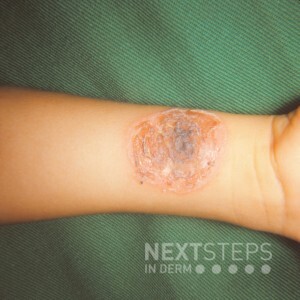
The patient’s arm shows a superficial erosion with serous crust, which is consistent with bullous impetigo. Caused by exfoliative toxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus, the primary lesion is a bulla; however, often only erosions and a collarette of scale are noted on exam. A wound culture will readily grow S. aureus to confirm the diagnosis. Cutaneous bacterial infections are more common in patients with atopic dermatitis due to impaired barrier function.
Treatment:
Limited disease can be treated with topical mupiricin ointment twice daily for 5 days.
Patients with widespread disease or systemic symptoms can be treated with oral antibiotics such as cephalexin, erythromycin, or clindamycin (if MRSA is suspected).
The primary lesions of scabies are erythematous papules and burrows found with a predilection for the hands, interwebs, and volar wrists. The areolae, umbilicus, and genitals are often involved.
A tzanck smear is performed to evaluate herpetic infections. Unlike the superficial erosions of bullous impetigo, herpetic infections produce punched out ulcerations.
A potassium hydroxide prep is performed when there is clinical suspicion of a fungal infection. Erosions are not characteristic findings of dermatophyte infections.
A punch biopsy is performed when the diagnosis is in question. Though a biopsy could confirm the diagnosis of bullous impetigo, the diagnosis can be confidently made by clinical evaluation and confirmed with a wound culture.
