The correct answer is C. Penicillin.
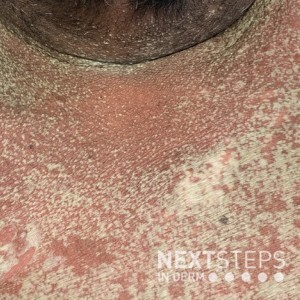
This clinical vignette is an acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), which classically presents numerous nonfollicular sterile pustules on the background of erythema starting in the intertriginous areas and face. The eruption rapidly expands to the trunk and extremities. Fever and leukocytosis are often present. The most common triggers of AGEP are antibiotics (aminopenicillins, macrolides), antifungals, calcium channel blockers like diltiazem, and antimalarials. Onset is rapid; eruption starts days after the administration of mediation. Resolution occurs spontaneously within 1-2 weeks after discontinuing the offending agent.
Allopurinol is associated with drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). TMP/SMX is associated with Steven Johnson syndrome/TEN and increases the risk of pancytopenia if administered with medication such as methotrexate. Hydralazine is associated with drug-induced systemic lupus.
References:
Bolognia, J., In Schaffer, J. V., & In Cerroni, L. Dermatology. Elsevier, 2018.
