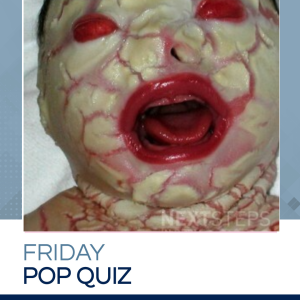
The correct answer is A. ABCA12 gene.
Mutations in the ABCA12 gene cause harlequin ichthyosis. X-linked ichthyosis (XLI) caused by a steroid sulfatase (STS) deficiency. Keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome is caused by a mutation in the GJB2 (connexin 26) gene. Ichthyosis vulgaris is caused by a defect in profilaggrin gene and lamellar ichthyosis involves a mutation in the gene for transglutaminase 1 (TGM1).
The inheritance of harlequin ichthyosis is autosomal recessive. It is due to mutations in the ABCA 12 (ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 12) gene. The ABCA12 gene is believed to encode a transporter protein involved in the transport of epidermal lipids across cell membranes and is essential for normal skin development.
Some mutations in the ABCA12 gene prevent the cell from making any ABCA12 protein. Other mutations lead to the production of an abnormally small version of the protein that cannot transport lipids properly. A loss of functional ABCA12 protein disrupts the normal development of the epidermis, resulting in the hard, thick scales characteristic of harlequin ichthyosis.
References:
Sutton JB. A case of general seborrhœa or “harlequin” fetus. Med Chir Trans 1886; 69: 291–96.1. PubMed Central.
Ahmed H, O’Toole EA. Recent advances in the genetics and management of harlequin ichthyosis. Pediatr Dermatol 2014; 31: 539–46. PubMed
Rajpopat S, Moss C, Mellerio J, et al. Harlequin ichthyosis: a review of clinical and molecular findings in 45 cases. Arch Dermatol 2011; 147: 681–6. DOI: 10.1001/archdermatol.2011.9. PubMed.
Kelsell DP, Norgett EE, Unsworth H et al. Mutations in ABCA12 underlie the severe congenital skin disease harlequin ichthyosis. Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 794–803. DOI: 10.1086/429844. PubMed Central.
Akiyama, M. ABCA12 mutations and autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis: a review of genotype/phenotype correlations and of pathogenetic concepts. Hum Mutat 2010; 31: 1090–6. DOI: 10.1002/humu.21326. PubMed.
Chang LM, Reyes M. A case of harlequin ichthyosis treated with isotretinoin. Dermatol Online J 2014; 20 (2): 7. Journal.
