Inverse Eruptive Syringoma in a Skin of Color Patient
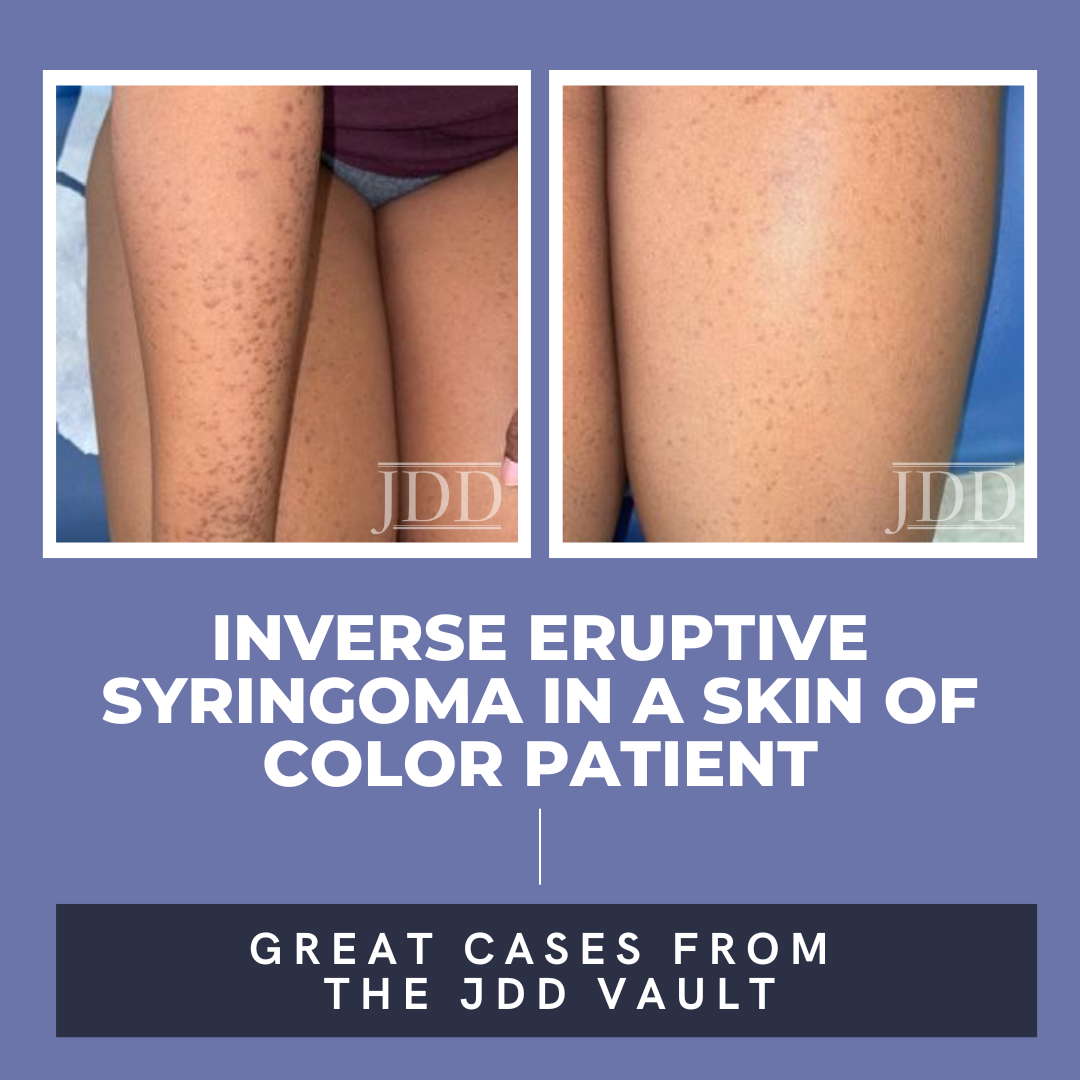 Syringomas are benign neoplasms derived from eccrine sweat glands. Eruptive syringomas are a subtype of syringomas and are typically located on the chest, neck, and abdomen during puberty or childhood. Herein, JDD authors Jennifer Wang BA, Nyousha Yousefi MD, Edward Heilman MD FAAD FCAP, and Jared Jagdeo MD MS present a 20-year-old African American female with an atypical case of eruptive syringom …
Syringomas are benign neoplasms derived from eccrine sweat glands. Eruptive syringomas are a subtype of syringomas and are typically located on the chest, neck, and abdomen during puberty or childhood. Herein, JDD authors Jennifer Wang BA, Nyousha Yousefi MD, Edward Heilman MD FAAD FCAP, and Jared Jagdeo MD MS present a 20-year-old African American female with an atypical case of eruptive syringom …
 Syringomas are benign neoplasms derived from eccrine sweat glands. Eruptive syringomas are a subtype of syringomas and are typically located on the chest, neck, and abdomen during puberty or childhood. Herein, JDD authors Jennifer Wang BA, Nyousha Yousefi MD, Edward Heilman MD FAAD FCAP, and Jared Jagdeo MD MS present a 20-year-old African American female with an atypical case of eruptive syringom …
Syringomas are benign neoplasms derived from eccrine sweat glands. Eruptive syringomas are a subtype of syringomas and are typically located on the chest, neck, and abdomen during puberty or childhood. Herein, JDD authors Jennifer Wang BA, Nyousha Yousefi MD, Edward Heilman MD FAAD FCAP, and Jared Jagdeo MD MS present a 20-year-old African American female with an atypical case of eruptive syringom … Continue reading "Inverse Eruptive Syringoma in a Skin of Color Patient"


 JDD authors Mihir Shah MD, Jenna Wald MD, and C. William Hanke MD MPH present a case of a patient with eruptive squamous cell carcinomas following treatment with Fludarabine to highlight not only the risk of cSCC in CLL patients and the increased risk for atypical cutaneous malignancies after treatment with systemic therapies such as fludarabine, but also to discuss treatment options for this …
JDD authors Mihir Shah MD, Jenna Wald MD, and C. William Hanke MD MPH present a case of a patient with eruptive squamous cell carcinomas following treatment with Fludarabine to highlight not only the risk of cSCC in CLL patients and the increased risk for atypical cutaneous malignancies after treatment with systemic therapies such as fludarabine, but also to discuss treatment options for this … 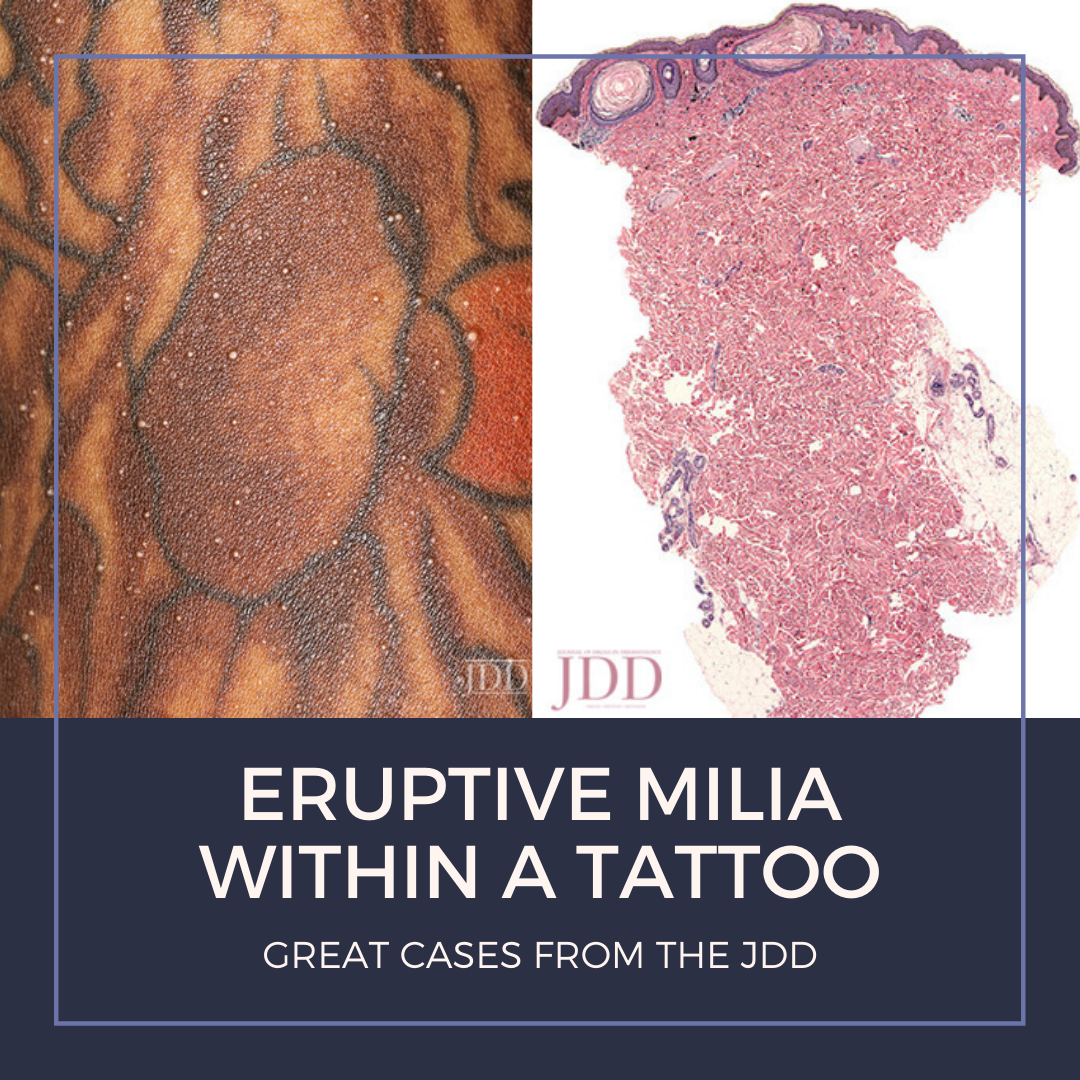 Introduction
The most frequently reported tattoo-related dermatoses, according to a study of 234 tattooed patients, are allergic,1infectious,2,3 and granulomatous4,5 reactions occurring in 2.1% of this population.6 Less common reactions are lichenoid,7photoallergic,8 pseudolymphomatous,9 discoid lupus erythematosus,10 incidental skin neoplasm,11 and koebnerization of psoriasis.12,13Milia within t …
Introduction
The most frequently reported tattoo-related dermatoses, according to a study of 234 tattooed patients, are allergic,1infectious,2,3 and granulomatous4,5 reactions occurring in 2.1% of this population.6 Less common reactions are lichenoid,7photoallergic,8 pseudolymphomatous,9 discoid lupus erythematosus,10 incidental skin neoplasm,11 and koebnerization of psoriasis.12,13Milia within t …  The May issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (JDD) focuses on skin cancer and includes the perfect blend of original articles and case reports. Topics include actinic keratosis versus squamous cell carcinoma, the utility of gene expression profiling in skin cancer, the prevalence of sunscreen use, and many more. Check out this month’s issue highlights straight from the JDD Editor’s …
The May issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology (JDD) focuses on skin cancer and includes the perfect blend of original articles and case reports. Topics include actinic keratosis versus squamous cell carcinoma, the utility of gene expression profiling in skin cancer, the prevalence of sunscreen use, and many more. Check out this month’s issue highlights straight from the JDD Editor’s …