Pigmented Lesion – Friday Pop Quiz 6/11
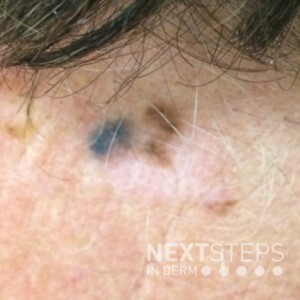 This patient presented for a different lesion but you see this during your exam and perform a biopsy. If the pigmented lesion seen here is 0.9mm deep, what is the recommended margin for excision?
A. <0.5cm
B. 0.5cm
C. 1.0cm
D. 2.0cm
E. >2.0cm
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Brought to you by our brand partner Derm In-Review. A …
This patient presented for a different lesion but you see this during your exam and perform a biopsy. If the pigmented lesion seen here is 0.9mm deep, what is the recommended margin for excision?
A. <0.5cm
B. 0.5cm
C. 1.0cm
D. 2.0cm
E. >2.0cm
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Brought to you by our brand partner Derm In-Review. A …
 This patient presented for a different lesion but you see this during your exam and perform a biopsy. If the pigmented lesion seen here is 0.9mm deep, what is the recommended margin for excision?
A. <0.5cm
B. 0.5cm
C. 1.0cm
D. 2.0cm
E. >2.0cm
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Brought to you by our brand partner Derm In-Review. A …
This patient presented for a different lesion but you see this during your exam and perform a biopsy. If the pigmented lesion seen here is 0.9mm deep, what is the recommended margin for excision?
A. <0.5cm
B. 0.5cm
C. 1.0cm
D. 2.0cm
E. >2.0cm
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Brought to you by our brand partner Derm In-Review. A … 

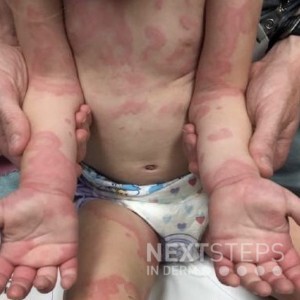 This healthy 2-year-old female presents with a 2-day history of the pruritic rash seen here. She had mild edema of the dorsal hands and feet and positive dermatographism on exam. All lesions were transient, lasting less than 24 hours in the same location. She was otherwise well and her parents denied any fever or systemic symptoms. What is the best diagnosis?
A. Serum sickness-like reaction …
This healthy 2-year-old female presents with a 2-day history of the pruritic rash seen here. She had mild edema of the dorsal hands and feet and positive dermatographism on exam. All lesions were transient, lasting less than 24 hours in the same location. She was otherwise well and her parents denied any fever or systemic symptoms. What is the best diagnosis?
A. Serum sickness-like reaction … 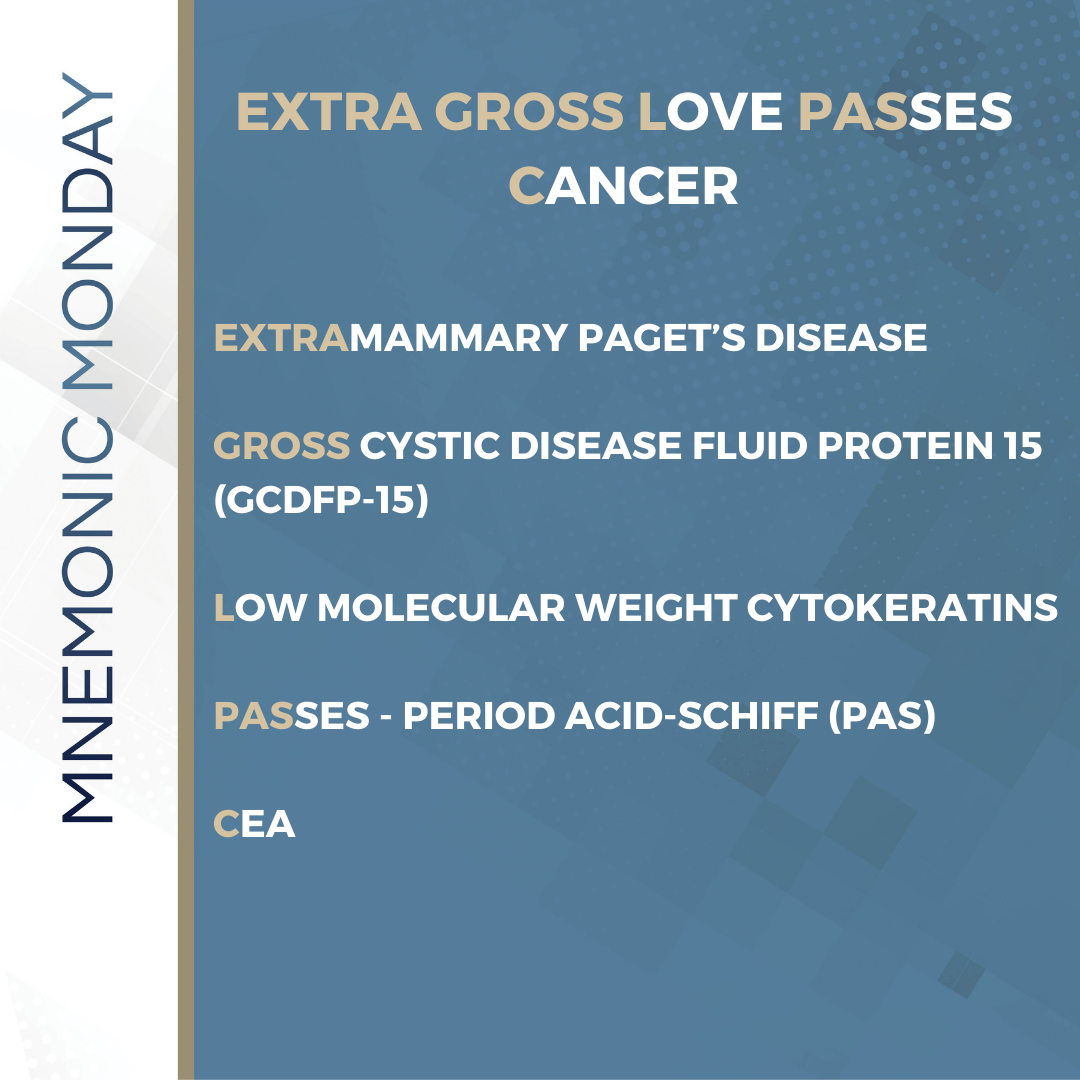 On this Mnemonic Monday, we challenge you to remember immunohistochemical markers for paget cells in Extramammary Paget’s Disease with the following mnemonic:
"EXTRA GROSS LOVE PASSES CANCER"
Extra- Extramammary Paget’s Disease
Gross- Gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15)
LOVE- Low molecular weight cytokeratins
PASses- Period acid-Schiff (PAS)
CANCER- CEA
The wo …
On this Mnemonic Monday, we challenge you to remember immunohistochemical markers for paget cells in Extramammary Paget’s Disease with the following mnemonic:
"EXTRA GROSS LOVE PASSES CANCER"
Extra- Extramammary Paget’s Disease
Gross- Gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15)
LOVE- Low molecular weight cytokeratins
PASses- Period acid-Schiff (PAS)
CANCER- CEA
The wo … 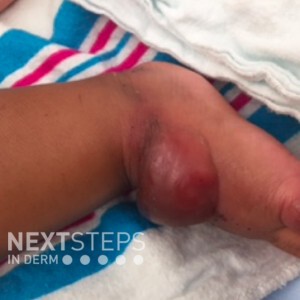 A 6-month old infant develops tense blisters on the distal extremities which develop on normal-appearing skin. He has a neurologic disease and has been immobilized for a long period of time. The blisters spontaneously heal within 1-2 weeks. You suspect a diagnosis of coma bullae. Which of the following is the key characteristic histologic feature that would assist you in making this diagnosis? …
A 6-month old infant develops tense blisters on the distal extremities which develop on normal-appearing skin. He has a neurologic disease and has been immobilized for a long period of time. The blisters spontaneously heal within 1-2 weeks. You suspect a diagnosis of coma bullae. Which of the following is the key characteristic histologic feature that would assist you in making this diagnosis? … 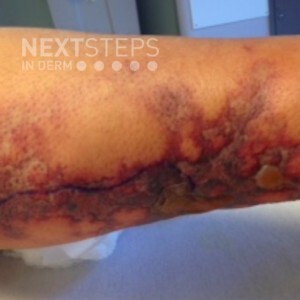 A 65-year-old female patient presents with poorly demarcated, symmetric, very painful patches of erythema and retiform purpura, favoring the thighs and buttocks. Bullae and a dusky gray discoloration developed, as well as the appearance of ulcerations with black, leathery eschars. A skin biopsy of the affected area is suggestive of calciphylaxis. Shortly after, she dies from secondary infectio …
A 65-year-old female patient presents with poorly demarcated, symmetric, very painful patches of erythema and retiform purpura, favoring the thighs and buttocks. Bullae and a dusky gray discoloration developed, as well as the appearance of ulcerations with black, leathery eschars. A skin biopsy of the affected area is suggestive of calciphylaxis. Shortly after, she dies from secondary infectio …