Basal Cell Carcinoma – Friday Pop Quiz 1/25
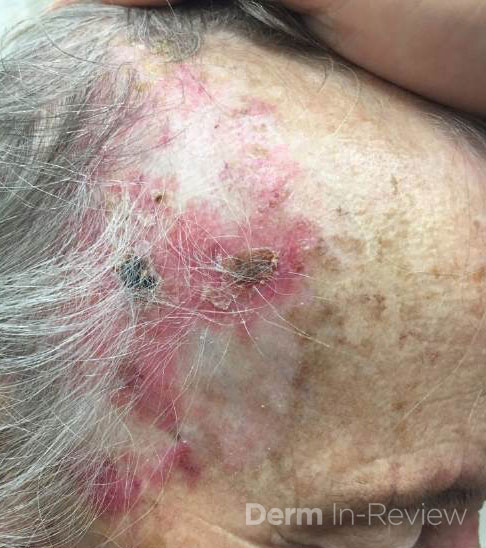 The patient had an extensive superficial basal cell carcinoma on the forehead treated with topical imiquimod and returned 4-weeks later with this reaction. Which cytokine is not activated by this medication?
A. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α
B. Interferon (IFN)-α
C. Interferon (IFN)-γ
D. Interleukin (IL)-12
E. Interleukin (IL)-4
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation …
The patient had an extensive superficial basal cell carcinoma on the forehead treated with topical imiquimod and returned 4-weeks later with this reaction. Which cytokine is not activated by this medication?
A. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α
B. Interferon (IFN)-α
C. Interferon (IFN)-γ
D. Interleukin (IL)-12
E. Interleukin (IL)-4
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation …
 The patient had an extensive superficial basal cell carcinoma on the forehead treated with topical imiquimod and returned 4-weeks later with this reaction. Which cytokine is not activated by this medication?
A. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α
B. Interferon (IFN)-α
C. Interferon (IFN)-γ
D. Interleukin (IL)-12
E. Interleukin (IL)-4
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation …
The patient had an extensive superficial basal cell carcinoma on the forehead treated with topical imiquimod and returned 4-weeks later with this reaction. Which cytokine is not activated by this medication?
A. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α
B. Interferon (IFN)-α
C. Interferon (IFN)-γ
D. Interleukin (IL)-12
E. Interleukin (IL)-4
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation … Continue reading "Basal Cell Carcinoma – Friday Pop Quiz 1/25"


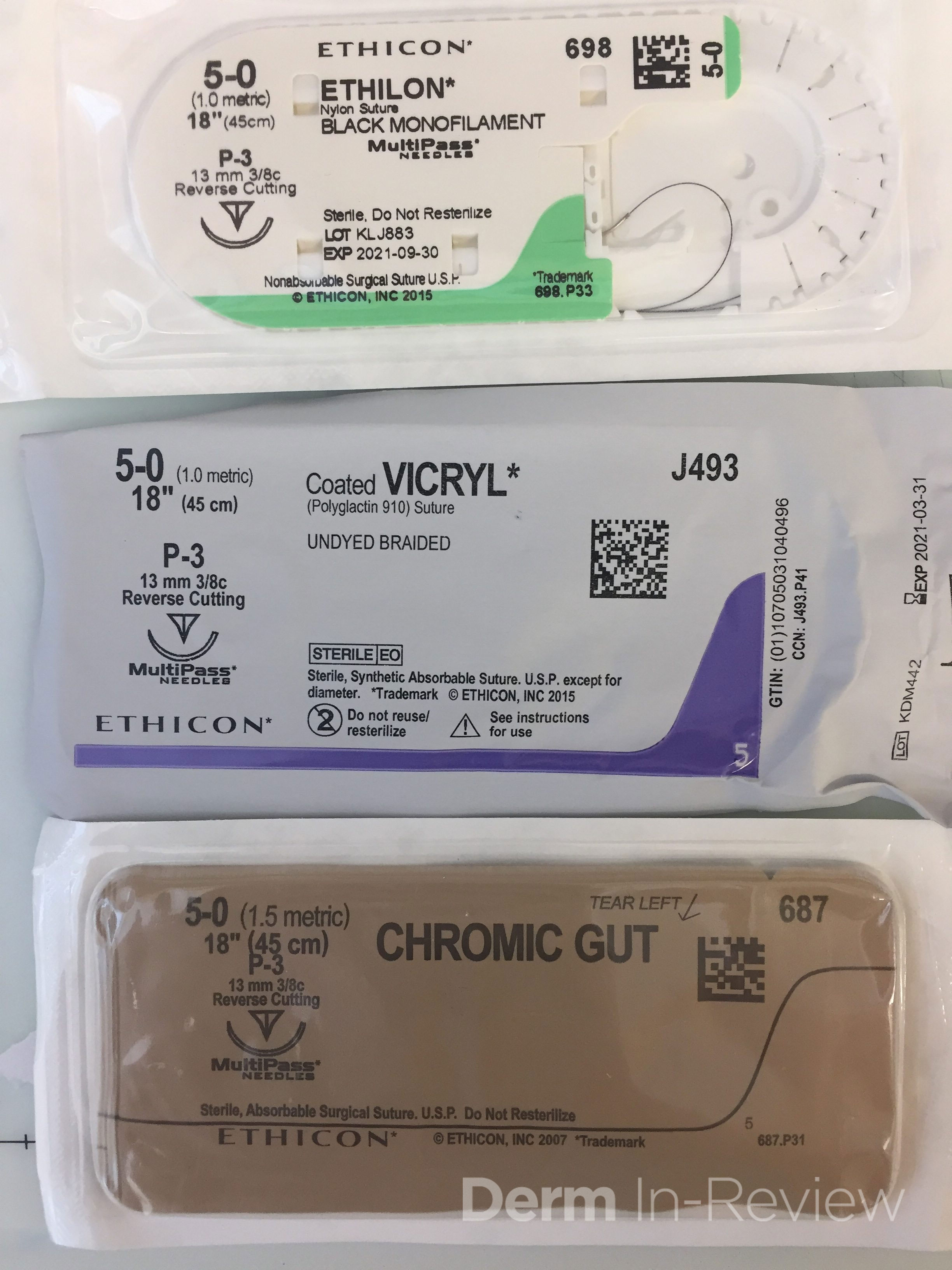 Which of the sutures shown here has the highest tissue reactivity?
A.) Chromic gut
B.) Polyglactin 910
C.) Polydioxanone
D.) Poliglecaprone 25
E.) Polyglycolic acid
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Want more? Continue testing your knowledge with more pop quizzes.
Take custom quizzes and simulated board exams here.
Brought to you by our Brand P …
Which of the sutures shown here has the highest tissue reactivity?
A.) Chromic gut
B.) Polyglactin 910
C.) Polydioxanone
D.) Poliglecaprone 25
E.) Polyglycolic acid
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Want more? Continue testing your knowledge with more pop quizzes.
Take custom quizzes and simulated board exams here.
Brought to you by our Brand P … 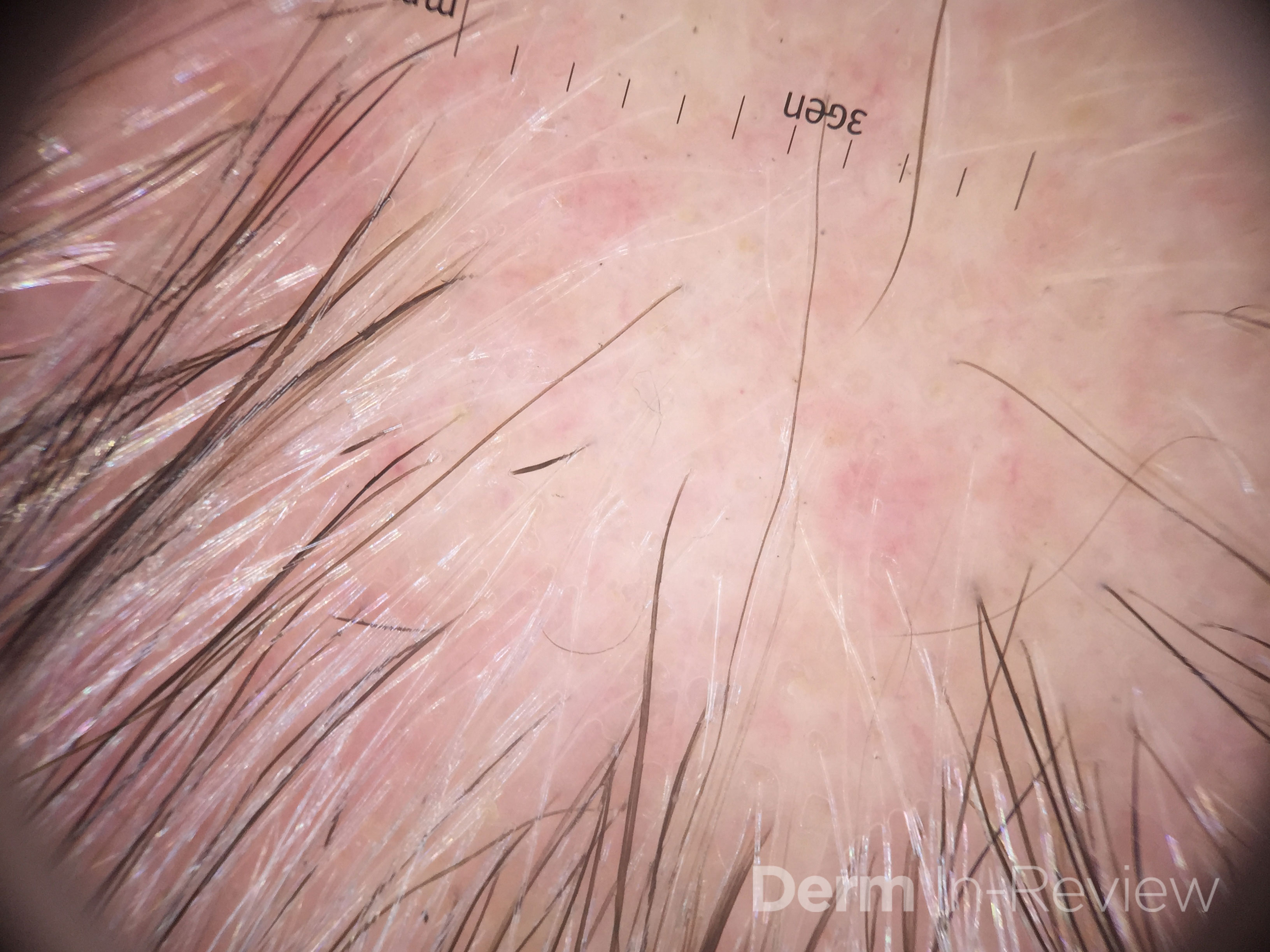 First line treatment for this condition includes:
A) Intralesional steroid injections
B) 2.4 million units IM benzathine penicillin
C) Methotrexate
D) Ruxolitinib
E) Treatment for underlying lymphoma
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Brought to you by our Brand Partner
…
First line treatment for this condition includes:
A) Intralesional steroid injections
B) 2.4 million units IM benzathine penicillin
C) Methotrexate
D) Ruxolitinib
E) Treatment for underlying lymphoma
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Brought to you by our Brand Partner
…  You would expect this neoplasm to:
A) Be painful on palpation
B) Have a high metastatic rate and poor prognosis
C) Disseminate to the skin from an internal focus
D) Dimple on lateral palpation
E) Have mutations in the SHH/PTCH signaling pathway
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Want more? Continue testing your knowledge with more pop quizzes.
Take …
You would expect this neoplasm to:
A) Be painful on palpation
B) Have a high metastatic rate and poor prognosis
C) Disseminate to the skin from an internal focus
D) Dimple on lateral palpation
E) Have mutations in the SHH/PTCH signaling pathway
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Want more? Continue testing your knowledge with more pop quizzes.
Take … 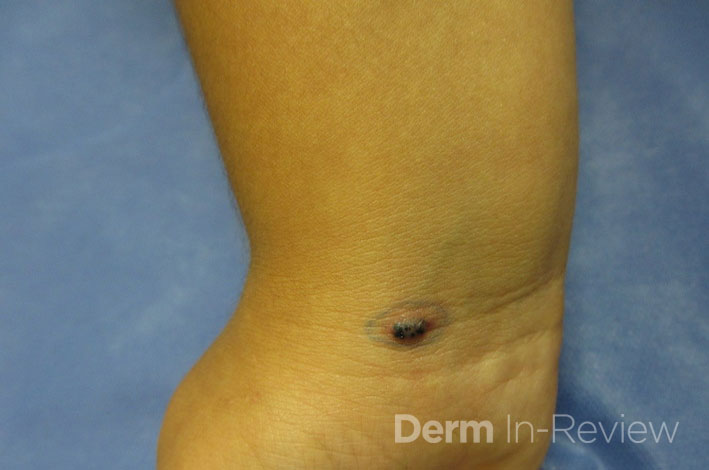 A patient presents with this lesion shown in the image. Which of the following are true?
A.) The patient has lymphangioma circumscriptum.
B.) The patient likley will develop renal and cardiac failure.
C.) The patient should be refered for genetic counceling for accumulation of glycosphingolipids.
D.) An excisional biopsy should be taken
E.) They are commonly related to trauma and requir …
A patient presents with this lesion shown in the image. Which of the following are true?
A.) The patient has lymphangioma circumscriptum.
B.) The patient likley will develop renal and cardiac failure.
C.) The patient should be refered for genetic counceling for accumulation of glycosphingolipids.
D.) An excisional biopsy should be taken
E.) They are commonly related to trauma and requir …