Topical Tacrolimus/Pimecrolimus Therapeutic Cheat Sheet
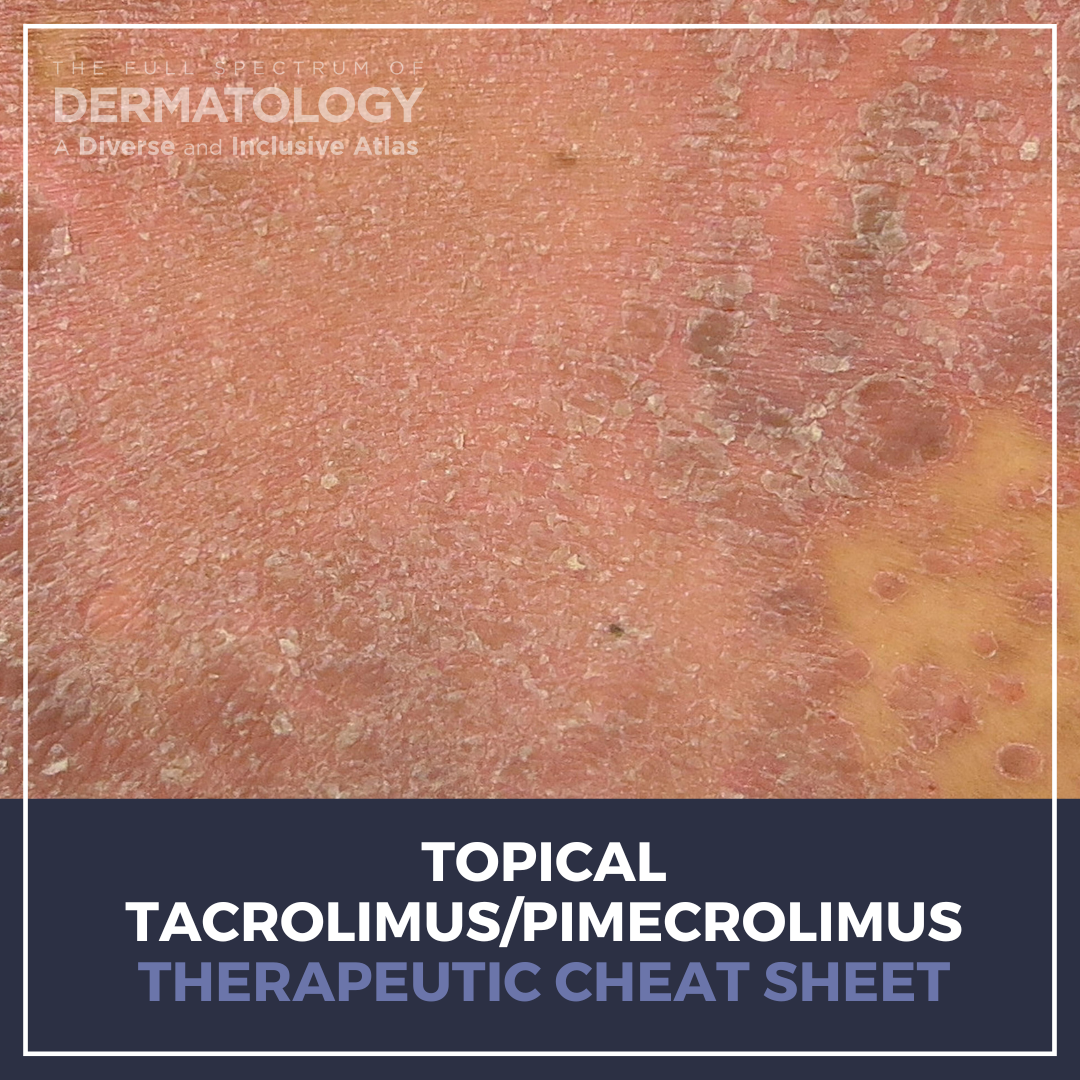 Tacrolimus and Pimecrolimus are both calcineurin inhibitors FDA-approved for atopic dermatitis. However, their topical use offers steroid-sparing benefits for a wide variety of other inflammatory dermatologic conditions. Tacrolimus was discovered in 1984 from the soil bacterium Streptomyces tsukubaensis and was originally FDA approved in 1994 as a systemic immunosuppressant for organ transplanta …
Tacrolimus and Pimecrolimus are both calcineurin inhibitors FDA-approved for atopic dermatitis. However, their topical use offers steroid-sparing benefits for a wide variety of other inflammatory dermatologic conditions. Tacrolimus was discovered in 1984 from the soil bacterium Streptomyces tsukubaensis and was originally FDA approved in 1994 as a systemic immunosuppressant for organ transplanta …
 Tacrolimus and Pimecrolimus are both calcineurin inhibitors FDA-approved for atopic dermatitis. However, their topical use offers steroid-sparing benefits for a wide variety of other inflammatory dermatologic conditions. Tacrolimus was discovered in 1984 from the soil bacterium Streptomyces tsukubaensis and was originally FDA approved in 1994 as a systemic immunosuppressant for organ transplanta …
Tacrolimus and Pimecrolimus are both calcineurin inhibitors FDA-approved for atopic dermatitis. However, their topical use offers steroid-sparing benefits for a wide variety of other inflammatory dermatologic conditions. Tacrolimus was discovered in 1984 from the soil bacterium Streptomyces tsukubaensis and was originally FDA approved in 1994 as a systemic immunosuppressant for organ transplanta … Continue reading "Topical Tacrolimus/Pimecrolimus Therapeutic Cheat Sheet"


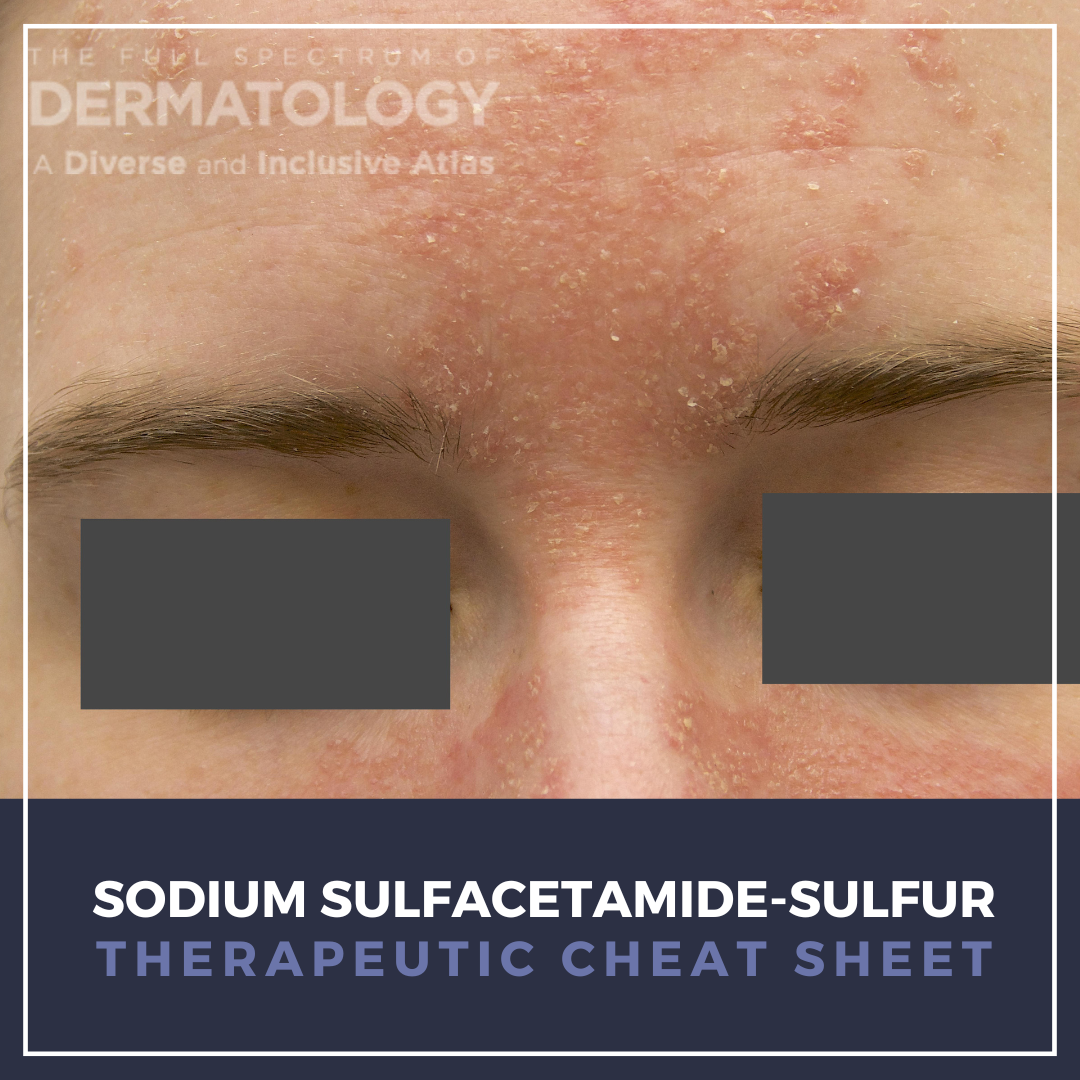 Sulfur–sulfacetamide is a long-standing topical therapy in dermatology valued for its combined antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and keratolytic effects. It is commonly used for several conditions including acne vulgaris, papulopustular rosacea, and seborrheic dermatitis. Although newer targeted therapies are often preferred for rosacea, sulfur–sulfacetamide remains a practical option, especia …
Sulfur–sulfacetamide is a long-standing topical therapy in dermatology valued for its combined antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and keratolytic effects. It is commonly used for several conditions including acne vulgaris, papulopustular rosacea, and seborrheic dermatitis. Although newer targeted therapies are often preferred for rosacea, sulfur–sulfacetamide remains a practical option, especia … 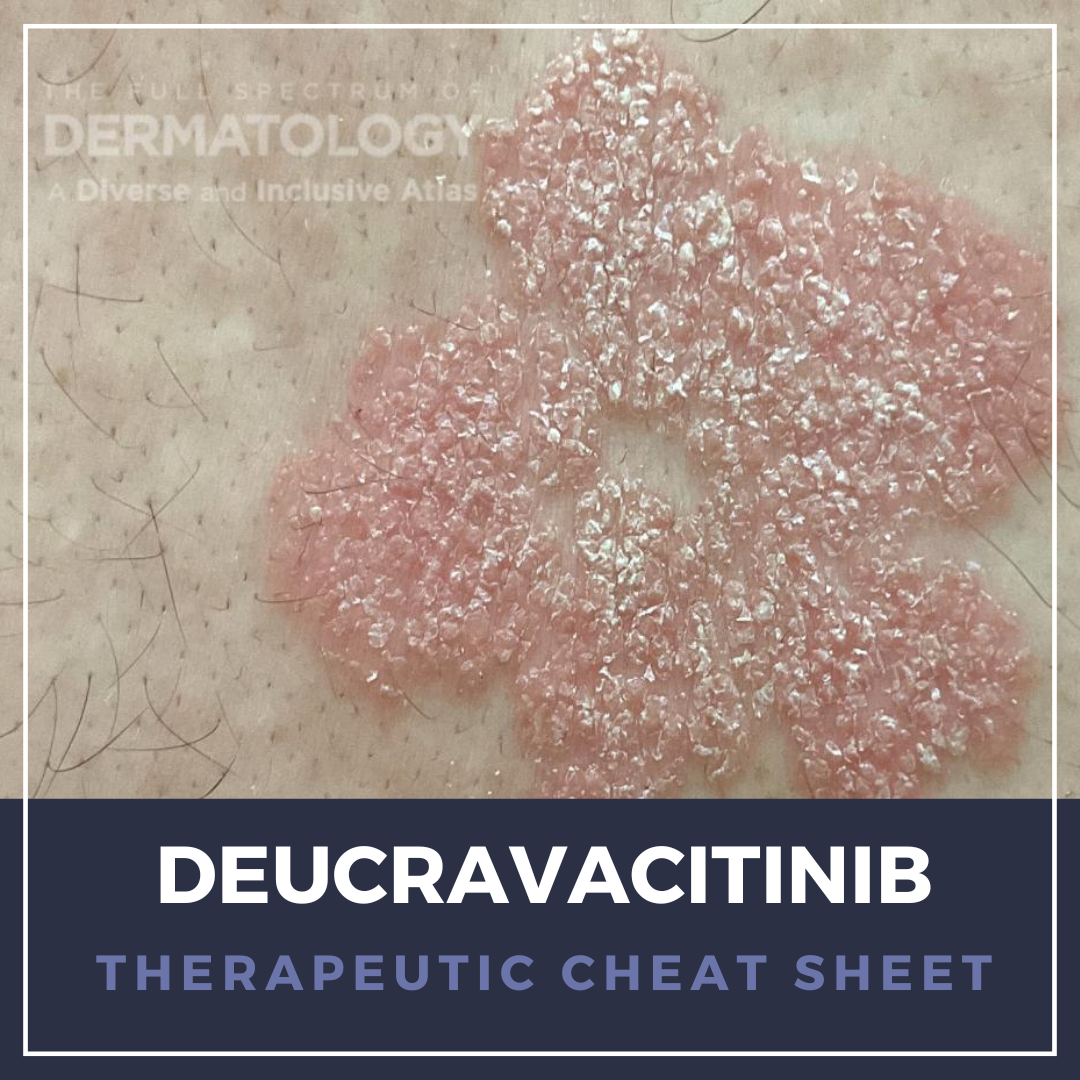 Psoriasis is one of the most common immune-mediated inflammatory dermatoses, with increasing evidence for systemic comorbidities. Targeted systemic agents have revolutionized the management of moderate-to-severe psoriasis, with life-changing outcomes for many patients with the chronic disease. Injectable biologics, blocking interleukin (IL)-23 or IL-17 cytokine pathways, have become invaluable opt …
Psoriasis is one of the most common immune-mediated inflammatory dermatoses, with increasing evidence for systemic comorbidities. Targeted systemic agents have revolutionized the management of moderate-to-severe psoriasis, with life-changing outcomes for many patients with the chronic disease. Injectable biologics, blocking interleukin (IL)-23 or IL-17 cytokine pathways, have become invaluable opt … 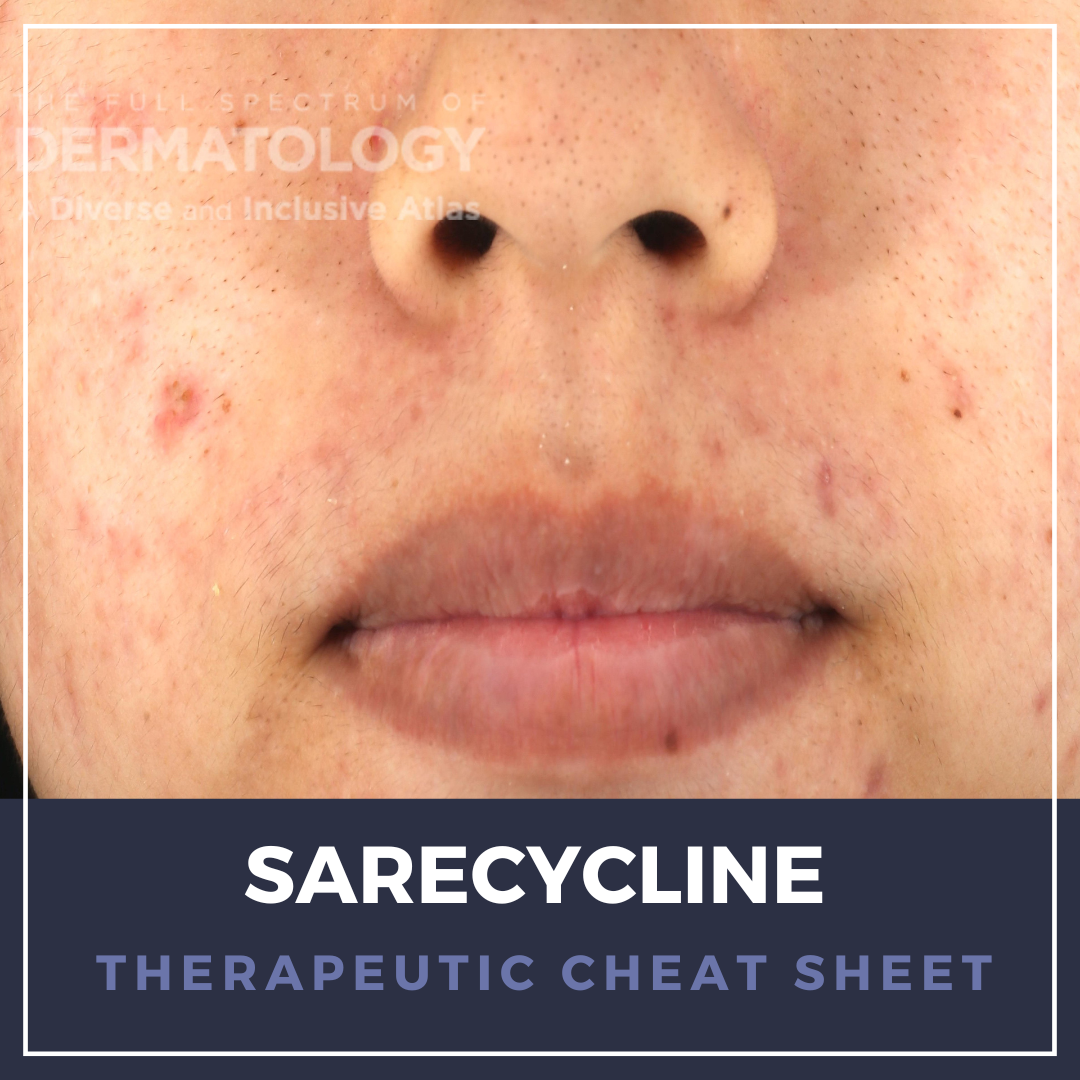 Sarecycline is a third-generation, narrow-spectrum tetracycline developed specifically for the treatment of acne vulgaris. It is distinguished by its weight-based once-daily dosing, favorable side effect profile, and relative microbiome-sparing compared with older tetracyclines. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a closer look at Sarecycline.
� …
Sarecycline is a third-generation, narrow-spectrum tetracycline developed specifically for the treatment of acne vulgaris. It is distinguished by its weight-based once-daily dosing, favorable side effect profile, and relative microbiome-sparing compared with older tetracyclines. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a closer look at Sarecycline.
� …  Cyclophosphamide, an alkylating agent introduced in the 1950s, has long served as a cornerstone therapy in rheumatology and oncology for its potent cytotoxic and immunosuppressive effects. In dermatology, it has been employed as a rescue agent for severe, refractory autoimmune and inflammatory skin diseases, particularly those associated with systemic connective tissue disorders. Its role spans co …
Cyclophosphamide, an alkylating agent introduced in the 1950s, has long served as a cornerstone therapy in rheumatology and oncology for its potent cytotoxic and immunosuppressive effects. In dermatology, it has been employed as a rescue agent for severe, refractory autoimmune and inflammatory skin diseases, particularly those associated with systemic connective tissue disorders. Its role spans co …