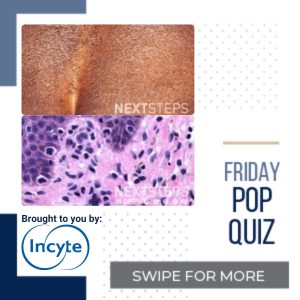
The correct answer is C. Loss of CD7 expression in the atypical T-cell infiltrate.
The correct answer is loss of CD7 expression in the atypical T-cell infiltrate. MF is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). MF histology depends heavily on the disease stage, with early MF resembling reactive lymphocytes without significant cytologically atypical cells; many cases of MF requires serial biopsies from different clinical sites. Classic MF is characterized by atypical CD3(+)/CD4(+)/CD45(+) mature memory T-lymphocytes. The main exception to the predominantly CD4(+) atypical lymphocytes is in hypopigmented MF, which has mainly CD8(+) cells. Other histologic features of MF include: small to intermediate-sized atypical lymphocytes with hyperchromatic nuclei surrounded by clear cytoplasm. The infiltrate can be localized in the papillary dermis and/or dermoepidermal junction. Frequently, atypical cells are seen in the epidermis. Pautrier microabscesses are clusters of malignant/atypical lymphocytes in the epidermis and is pathognomonic for MF; however, Pautrier micro abscess is only seen in 25% of MF cases. The loss of T-cell surface antigen such as CD2, CD5, and CD7 is common and suggests disease progression. Of note, the loss of CD7 is considered a sensitive and specific finding in MF.
CD3 is a pan-T cell marker and would be positive in most cases of CTCL/MF. MF most commonly have atypical CD4(+) lymphocytes. Atypical CD8(+) T-cells is seen in hypopigmented MF, most MF cases are CD4(+). CD30(+) cells would suggest lymphomatoid papulosis or MF undergoing large cell transformation.
References:
Jawed SI, Myskowski PL, Horwitz S, Moskowitz A, Querfeld C. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part I. Diagnosis: clinical and histopathologic features and new molecular and biologic markers. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(2):205.e1-222. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.049
Bergman R, Faclieru D, Sahar D, et al. Immunophenotyping and T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangement analysis as an adjunct to the histopathologic diagnosis of mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998;39(4 Pt 1):554-559. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(98)70003-9
Hinds GA, Heald P. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009;60(3):359-378. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2008.10.031
Brought to you by our brand partner

