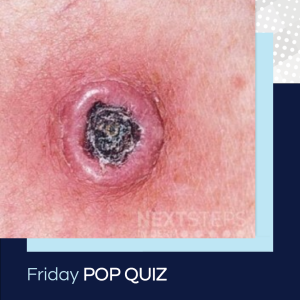
The correct answer is A. Ferguson-Smith.
Patients that have a sudden appearance during childhood of multiple keratoacanthomas have Ferguson-Smith type of KA. This is autosomal dominant and are the KAs are typically self-healing.
Grzybowski is typically diagnosed in adulthood with the sudden appearance of hundreds to thousands of lesions in a disseminated fashion. Gorlin syndrome is characterized by the appearance of multiple BCCs (not KAs) during childhood. It is also characterized by odontogenic keratocysts of the jaw and skeletal defects (e.g., macrocephaly, hypertelorism, frontoparietal bossing, spina bifida, or rib abnormality, among others). Tumors associated with this disease include medulloblastoma, meningioma, ovarian fibromas (bilateral), and cardiac fibromas. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, and due to a mutation in PTCH gene. KA centrifugum is a subtype of solitary KA that may reach a size of up to 20 cm in diameter. Buschke-Lowenstein tumor is a verrucous carcinoma caused by HPV 6 and 11 that is locally invasive and destructive but rarely metastatic.
References:
Cerroni L, Kerl H. Keratoacanthoma. In IM Freedberg, AZ Eisen, K Wolff, et al., Eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2003; 760-767.
Shwartz RA. Keratoacanthoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 1994; 30: 1-19.
