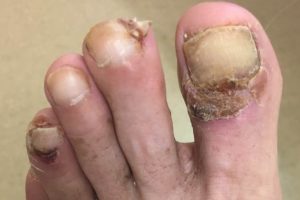
Correct Answer: A. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor
Explanation: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors cause a variety of cutaneous adverse reactions including paronychia, papulopustular (acneiform) eruption, photosensitivity, skin fragility, and hair changes. TNF inhibitors may be associated with injection site reactions and paradoxical psoriasiform eruptions. Smoothened inhibitors are associated with muscle spasm, alopecia, and dysgeusia. BRAF inhibitors are associated with maculopapular eruptions, photosensitivity, seborrheic dermatitis-like eruptions, keratosis pilaris-like eruptions and squamoproliferative growths. PD-1 inhibitors are associated with maculopapular eruptions, pruritus, lichenoid exanthema, and vitiligo.
Test your knowledge with custom quizzes at Derm In-Review or check out more pop quizzes.
Brought to you by our Brand Partner
![]()
Reference:
Macdonal JB, et al. Cutaneous adverse effects of targeted therapies Part I: Inhibitors of the cellular membrane. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72:203-18.
Associated DIR Sections: Dermatopharmacology
