Correct Answer: A
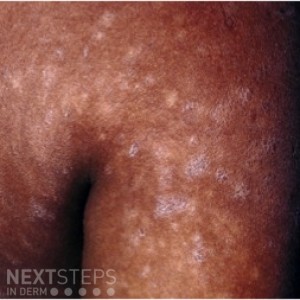
The image shows pityriasis lichenoides chronica (PLC), a rare, chronic cutaneous disorder most commonly seen in children and young adults with a slight male predominance. PLC presents with a widespread eruption comprised of scaly, red-brown papules and plaques that resolve with hypopigmentation. Both pityriasis lichenoides at varioliformis acute (PLEVA) and PLC contain lesional T cell infiltrates, with a general predominance of CD8+ T cells in PLEVA and CD4+ cells in PLC.
Choice 2 is incorrect as this describes pityriasis rosea, which has been associated with reactivation of HHV-6/HHV-7. Choice 3 is incorrect as this describes tinea versicolor, which is caused by growth of dimorphic yeast of the Malassezia genus. Choice 4 is incorrect as this describes phrynoderma, which is due to deficiency in vitamin A metabolism. Choice 5 is incorrect as this describes guttate psoriasis, which has been associated with preceding streptococcal pharyngitis.
References: Bolognia, Jean., Jorizzo, Joseph L.Schaffer, Julie V. (Eds.) (2012) Dermatology /[Philadelphia] : Elsevier Saunders, https://www.visualdx.com/visualdx/diagnosis/pityriasis+lichenoides+chronica?diagnosisId=52174&moduleId=101
