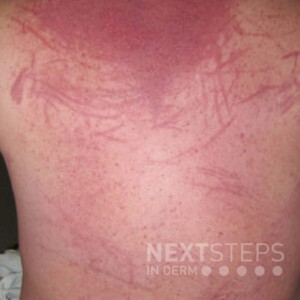
The correct answer is D. Dermatomyositis.
Manifestations of dermatomyositis range from poikiloderma of the scalp to centripetal flagellate erythema to erosions and ulcerations. It is also important to look for dermatologic signs of other connective tissue diseases in patients with dermatomyositis, because of the frequency of overlap syndromes. The most common cutaneous findings would be signs of overlap with systemic sclerosis, especially limited disease with CREST features (calcinosis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, telangiectasias), annular lesions suggestive of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus, or nodules suggestive of rheumatoid arthritis. Cutaneous small vessel vasculitis can occur as an associated finding, especially in patients with juvenile dermatomyositis.
In systemic lupus erythematosus, patients develop malar erythema, photosensitivity, and oral ulcers. Systemic sclerosis is characterized by Raynaud’s phenomenon acral or diffuse sclerosis, esophageal dysmotility, and pulmonary disease. Sarcoidosis can present with lupus pernio, erythema nodosum, and violaceous, indurated plaques. Behcet’s disease presents with recurrent oral and genital ulcerations, eye lesions, and skin lesions (erythema nodosum, pseudofolliculitis, papulopustular lesions, or acneiform nodules).
References:
Callen JP, Wortman RL. Dermatomyositis. Clinical Dermatolo. Sept-Oct 2006; 24(5) 363-73.
