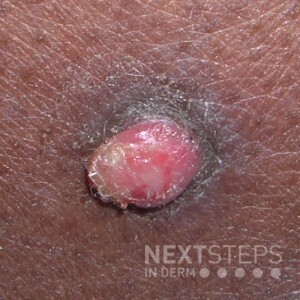
The correct answer is A. Erythromycin.
Bartonella hensalae is the causative agent of bacillary angiomatosis. The differential diagnosis of bacillary angiomatosis may include pyogenic granulomas and Kaposi’s sarcoma. Bacillary angiomatosis is effectively treated with antibiotics. Erythromycin appears to be the antibiotic of choice and is given until lesions resolve, usually within 3-4 weeks of starting therapy.
In addition to antibiotics, large pus-filled lymph nodes or blisters may need to be drained. Supportive therapy includes hydration and analgesics for pain and fever. Warm moist compresses to affected nodes may decrease swelling and tenderness.
Other antibiotics used include doxycycline, trimethoprim + sulphamethoxazole, tetracyclines, and rifampicin. Clindamycin, ceftriaxone, and fluconazole are not typical treatments of choice for this disease.
References:
Lins KA, Drummond MR, Velho PENF. Cutaneous manifestations of bartonellosis. An Bras Dermatol. 2019;94(5):594-602. doi:10.1016/j.abd.2019.09.024
