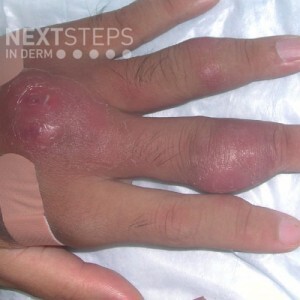
The correct answer is C. Minocycline.
Sporotrichoid spread may be seen in cutaneous leishmaniasis, actinomycosis, atypical mycobacterial infections, deep fungal infection, and melanoma. Mycobacterium marinum is associated with skin injury followed by exposure to contaminated water, usually from an aquarium, lake, or pool. The treatment of choice for M. marinum infections is minocycline or clarithromycin can be used empirically.
Penicillin is not a preferred agent in any mycobacterial infection – but is first line in syphilis.
Ceftriaxone is not a preferred agent in any mycobacterial infection – it can be a first line agent in gonorrhea and other infections.
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxasole is a second-line agent in M. marinum infection. It is also useful for MRSA infections. Cephalexin is not a preferred agent in any mycobacterial infection. It is a first-line agent in prophylaxis agent surgical site infections in those at high-risk. It is important to remember that the efficacy of prophylactic antibiotics in surgical site infections is tied to the medication having reached high plasma levels by the time of first incision (ie: it must be given in advance of the procedure).
References: In Bolognia, J., In Schaffer, J. V., & In Cerroni, L. (2018). Dermatology.
