Hypochlorous Acid for a Persistent Filler Nodule: A Case Report
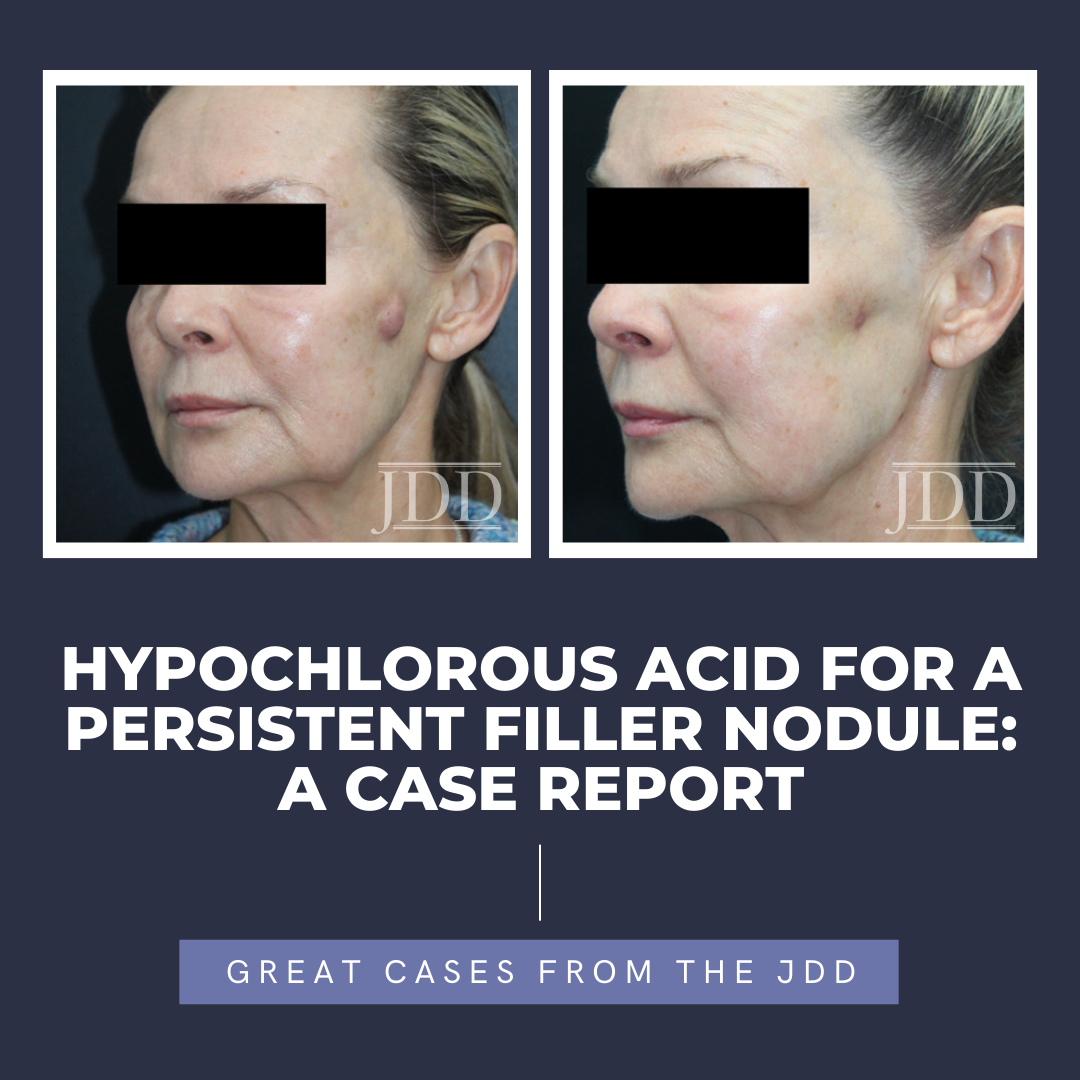 Hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers are widely used in aesthetic medicine for facial rejuvenation, volumization, and wrinkle treatment. Noninflammatory nodules after HA filler injection are a relatively common phenomenon and a result of poor technique or a large volume bolus in one area.¹ Unlike these nodules, delayed-onset nodules (DON) occur in 0.5% of injections and can be inflammatory, granulomatou …
Hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers are widely used in aesthetic medicine for facial rejuvenation, volumization, and wrinkle treatment. Noninflammatory nodules after HA filler injection are a relatively common phenomenon and a result of poor technique or a large volume bolus in one area.¹ Unlike these nodules, delayed-onset nodules (DON) occur in 0.5% of injections and can be inflammatory, granulomatou …
 Hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers are widely used in aesthetic medicine for facial rejuvenation, volumization, and wrinkle treatment. Noninflammatory nodules after HA filler injection are a relatively common phenomenon and a result of poor technique or a large volume bolus in one area.¹ Unlike these nodules, delayed-onset nodules (DON) occur in 0.5% of injections and can be inflammatory, granulomatou …
Hyaluronic acid (HA) fillers are widely used in aesthetic medicine for facial rejuvenation, volumization, and wrinkle treatment. Noninflammatory nodules after HA filler injection are a relatively common phenomenon and a result of poor technique or a large volume bolus in one area.¹ Unlike these nodules, delayed-onset nodules (DON) occur in 0.5% of injections and can be inflammatory, granulomatou … Continue reading "Hypochlorous Acid for a Persistent Filler Nodule: A Case Report"


 INTRODUCTION
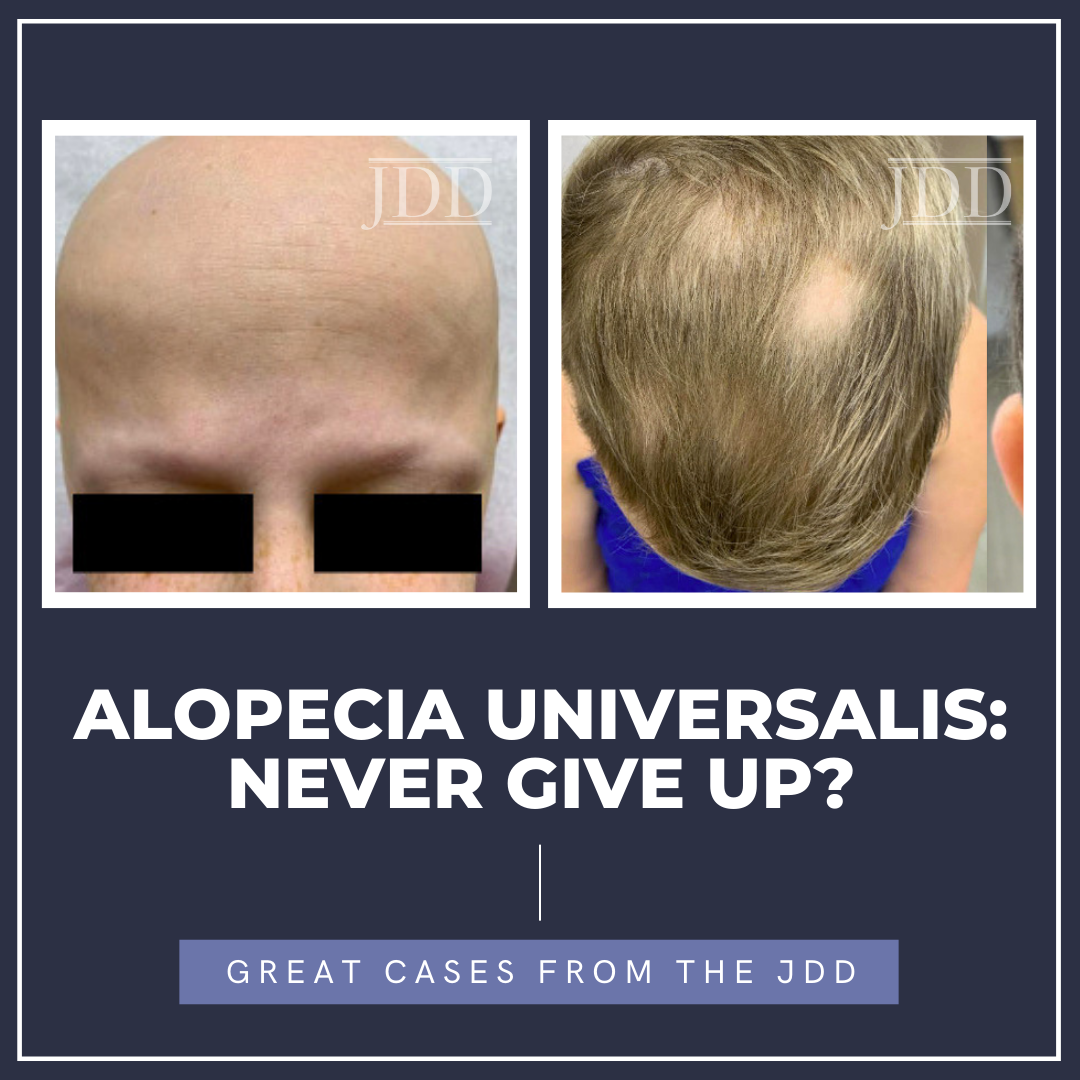
Alopecia universalis is a type of alopecia areata (AA) characterized by total body hair loss. The mechanism of this loss is primarily due to autoimmune disruption of the hair follicle. AA has historically been treated with corticosteroids, minoxidil, and other immune therapies that possess limited efficacy with high recurrence rates and adverse effects.1 However, in recent years the …
INTRODUCTION
Alopecia universalis is a type of alopecia areata (AA) characterized by total body hair loss. The mechanism of this loss is primarily due to autoimmune disruption of the hair follicle. AA has historically been treated with corticosteroids, minoxidil, and other immune therapies that possess limited efficacy with high recurrence rates and adverse effects.1 However, in recent years the … 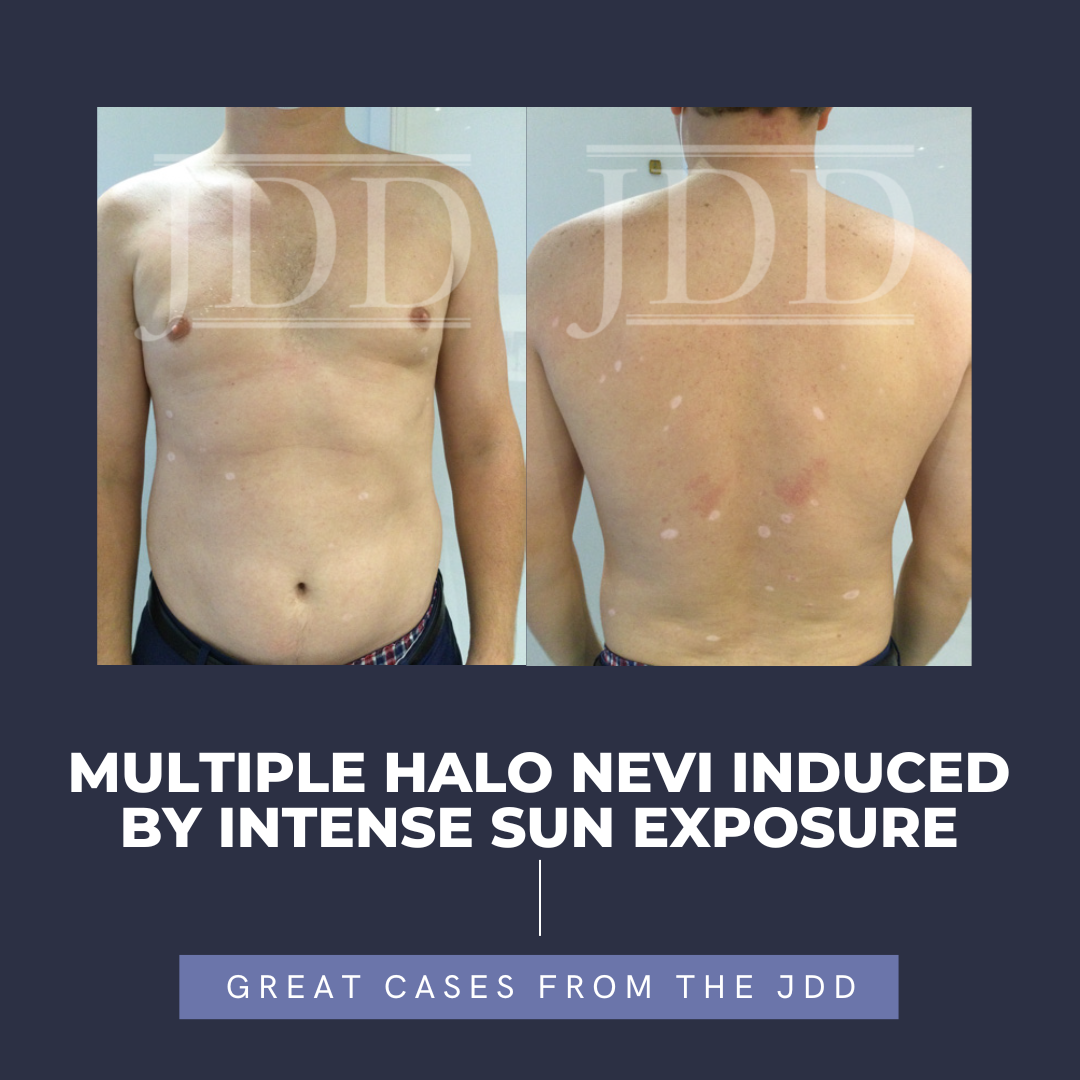 JDD authors present the case of a 38-year-old male who reported to their practice with multiple newly developed halos around 26 existing nevi on his trunk. The halo nevi developed after the patient, who lived in the northeast, spent 2 months on a lake in Alabama, with intense heat and sun exposure. This case is remarkable in that it points to ultraviolet exposure as one instigating factor in the …
JDD authors present the case of a 38-year-old male who reported to their practice with multiple newly developed halos around 26 existing nevi on his trunk. The halo nevi developed after the patient, who lived in the northeast, spent 2 months on a lake in Alabama, with intense heat and sun exposure. This case is remarkable in that it points to ultraviolet exposure as one instigating factor in the …  JDD authors Mihir Shah MD, Jenna Wald MD, and C. William Hanke MD MPH present a case of a patient with eruptive squamous cell carcinomas following treatment with Fludarabine to highlight not only the risk of cSCC in CLL patients and the increased risk for atypical cutaneous malignancies after treatment with systemic therapies such as fludarabine, but also to discuss treatment options for this …
JDD authors Mihir Shah MD, Jenna Wald MD, and C. William Hanke MD MPH present a case of a patient with eruptive squamous cell carcinomas following treatment with Fludarabine to highlight not only the risk of cSCC in CLL patients and the increased risk for atypical cutaneous malignancies after treatment with systemic therapies such as fludarabine, but also to discuss treatment options for this …  In this brief communication, JDD authors T. Roxana Ghadimi BS, Michael J. Martinez BS, and Evan A. Rieder MD present self-reported long-term, remote side effects to isotretinoin that dermatologists must be aware of.
INTRODUCTION
Isotretinoin is considered the gold standard treatment for severe nodulocystic acne, though it has been the subject of controversy in the media for concerns relate …
In this brief communication, JDD authors T. Roxana Ghadimi BS, Michael J. Martinez BS, and Evan A. Rieder MD present self-reported long-term, remote side effects to isotretinoin that dermatologists must be aware of.
INTRODUCTION
Isotretinoin is considered the gold standard treatment for severe nodulocystic acne, though it has been the subject of controversy in the media for concerns relate …