Patient Buzz: Rare Pediatric Skin Conditions | The Expert Weighs In
 Parade and other media outlets recently covered the story of actress Mandy Moore's son, who was diagnosed with Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. What should dermatology clinicians know about Gianotti-Crosti syndrome and other rare pediatric skin conditions? What should dermatology clinicians do when they are unsure of how to diagnose a pediatric skin condition?
For expert advice, I reached out to …
Parade and other media outlets recently covered the story of actress Mandy Moore's son, who was diagnosed with Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. What should dermatology clinicians know about Gianotti-Crosti syndrome and other rare pediatric skin conditions? What should dermatology clinicians do when they are unsure of how to diagnose a pediatric skin condition?
For expert advice, I reached out to …
 Parade and other media outlets recently covered the story of actress Mandy Moore's son, who was diagnosed with Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. What should dermatology clinicians know about Gianotti-Crosti syndrome and other rare pediatric skin conditions? What should dermatology clinicians do when they are unsure of how to diagnose a pediatric skin condition?
For expert advice, I reached out to …
Parade and other media outlets recently covered the story of actress Mandy Moore's son, who was diagnosed with Gianotti-Crosti syndrome. What should dermatology clinicians know about Gianotti-Crosti syndrome and other rare pediatric skin conditions? What should dermatology clinicians do when they are unsure of how to diagnose a pediatric skin condition?
For expert advice, I reached out to … Continue reading "Patient Buzz: Rare Pediatric Skin Conditions | The Expert Weighs In"


 Rituximab was the first monoclonal antibody approved for cancer treatment and now in dermatology, this medication has been life-altering for patients with the severe, autoimmune blistering disease, pemphigus vulgaris. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a closer look at rituximab, which is FDA-approved for the treatment of pemphigus vulgaris, and is also used off label for other …
Rituximab was the first monoclonal antibody approved for cancer treatment and now in dermatology, this medication has been life-altering for patients with the severe, autoimmune blistering disease, pemphigus vulgaris. We continue our series, Therapeutic Cheat Sheet, with a closer look at rituximab, which is FDA-approved for the treatment of pemphigus vulgaris, and is also used off label for other … 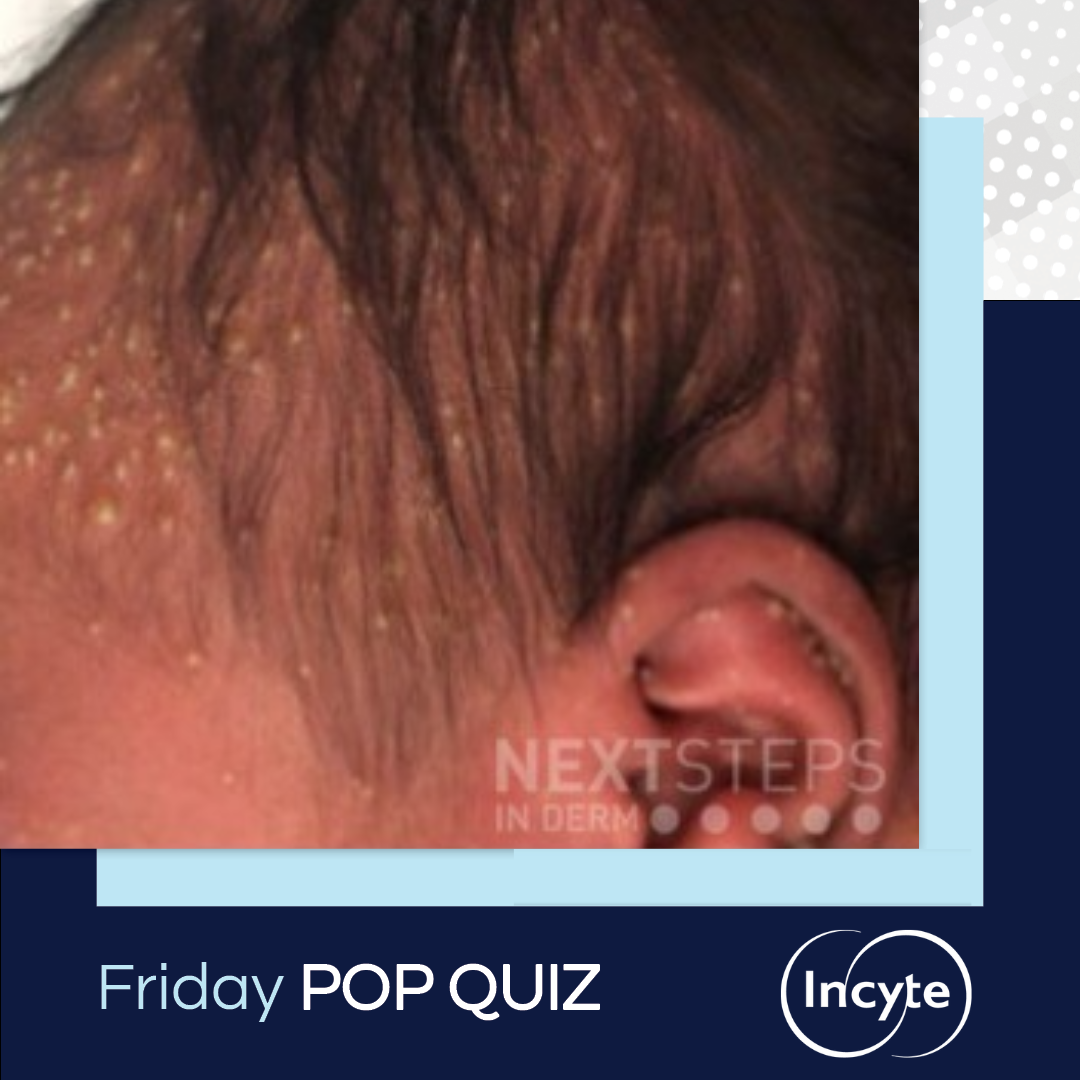 Which of the following cell types is most likely to be found on a Wright-Giemsa stain of fluid from the lesions shown on this 2-day-old child?
A. Basophils
B. Eosinophils
C. Histiocytes
D. Mast cells
E. Neutrophils
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Brought to you by our brand partner
…
Which of the following cell types is most likely to be found on a Wright-Giemsa stain of fluid from the lesions shown on this 2-day-old child?
A. Basophils
B. Eosinophils
C. Histiocytes
D. Mast cells
E. Neutrophils
To find out the correct answer and read the explanation, click here.
Brought to you by our brand partner
…  Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference, interviewed Dr. Kalyani Marathe, director of the dermatology division at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital. Dr. Marathe shares serious pediatric skin issues including infections, drug reactions and congenital conditions. Watch and learn how to recognize and treat these serious issues, and how to know whe …
Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference, interviewed Dr. Kalyani Marathe, director of the dermatology division at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital. Dr. Marathe shares serious pediatric skin issues including infections, drug reactions and congenital conditions. Watch and learn how to recognize and treat these serious issues, and how to know whe … 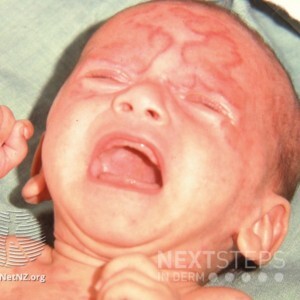 A 2 day-old infant is being seen in the hospital for the following rash. Which of the following is not true about the infant’s disease?
A. Skin lesions typically resolve without scarring
B. There is a strong association with anti-SSA/Ro antibodies
C. There are also reports of the presence of U1RNP antibodies
D. Lesions have a predilection for the face
E. Heart block often deve …
A 2 day-old infant is being seen in the hospital for the following rash. Which of the following is not true about the infant’s disease?
A. Skin lesions typically resolve without scarring
B. There is a strong association with anti-SSA/Ro antibodies
C. There are also reports of the presence of U1RNP antibodies
D. Lesions have a predilection for the face
E. Heart block often deve …