A Massive Case of Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
 ABSTRACT
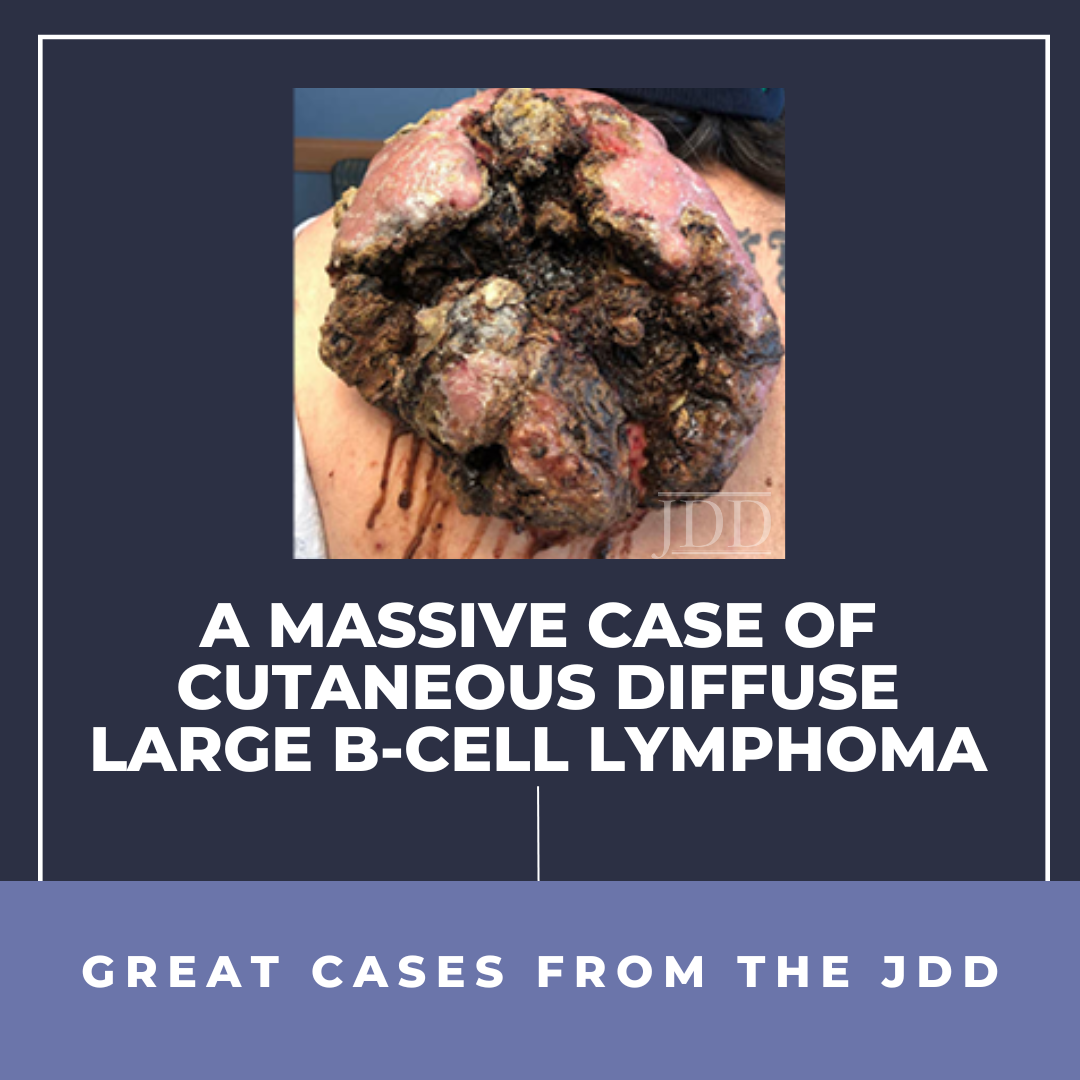
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and extranodal involvement is seen in approximately 40% of cases. However, cases involving the skin and muscle are rare, and skin manifestations most commonly present as plaques, papules, small nodules, or ulcers. In this report, JDD authors Lauren E. Merz MD MSc, Christopher B. Hergott MD PhD, and Reb …
ABSTRACT
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and extranodal involvement is seen in approximately 40% of cases. However, cases involving the skin and muscle are rare, and skin manifestations most commonly present as plaques, papules, small nodules, or ulcers. In this report, JDD authors Lauren E. Merz MD MSc, Christopher B. Hergott MD PhD, and Reb …
 ABSTRACT
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and extranodal involvement is seen in approximately 40% of cases. However, cases involving the skin and muscle are rare, and skin manifestations most commonly present as plaques, papules, small nodules, or ulcers. In this report, JDD authors Lauren E. Merz MD MSc, Christopher B. Hergott MD PhD, and Reb …
ABSTRACT
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and extranodal involvement is seen in approximately 40% of cases. However, cases involving the skin and muscle are rare, and skin manifestations most commonly present as plaques, papules, small nodules, or ulcers. In this report, JDD authors Lauren E. Merz MD MSc, Christopher B. Hergott MD PhD, and Reb … Continue reading "A Massive Case of Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma"


 March into groundbreaking dermatological insights with the latest issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology! Explore the prescribing habits of oral minoxidil for androgenetic alopecia, delve into a comprehensive review of botulinum toxin uses, and discover the effectiveness of microneedling for acne scars. Plus, unravel the uncertainties surrounding exosome therapy in androgenetic alopecia. Fro …
March into groundbreaking dermatological insights with the latest issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology! Explore the prescribing habits of oral minoxidil for androgenetic alopecia, delve into a comprehensive review of botulinum toxin uses, and discover the effectiveness of microneedling for acne scars. Plus, unravel the uncertainties surrounding exosome therapy in androgenetic alopecia. Fro … 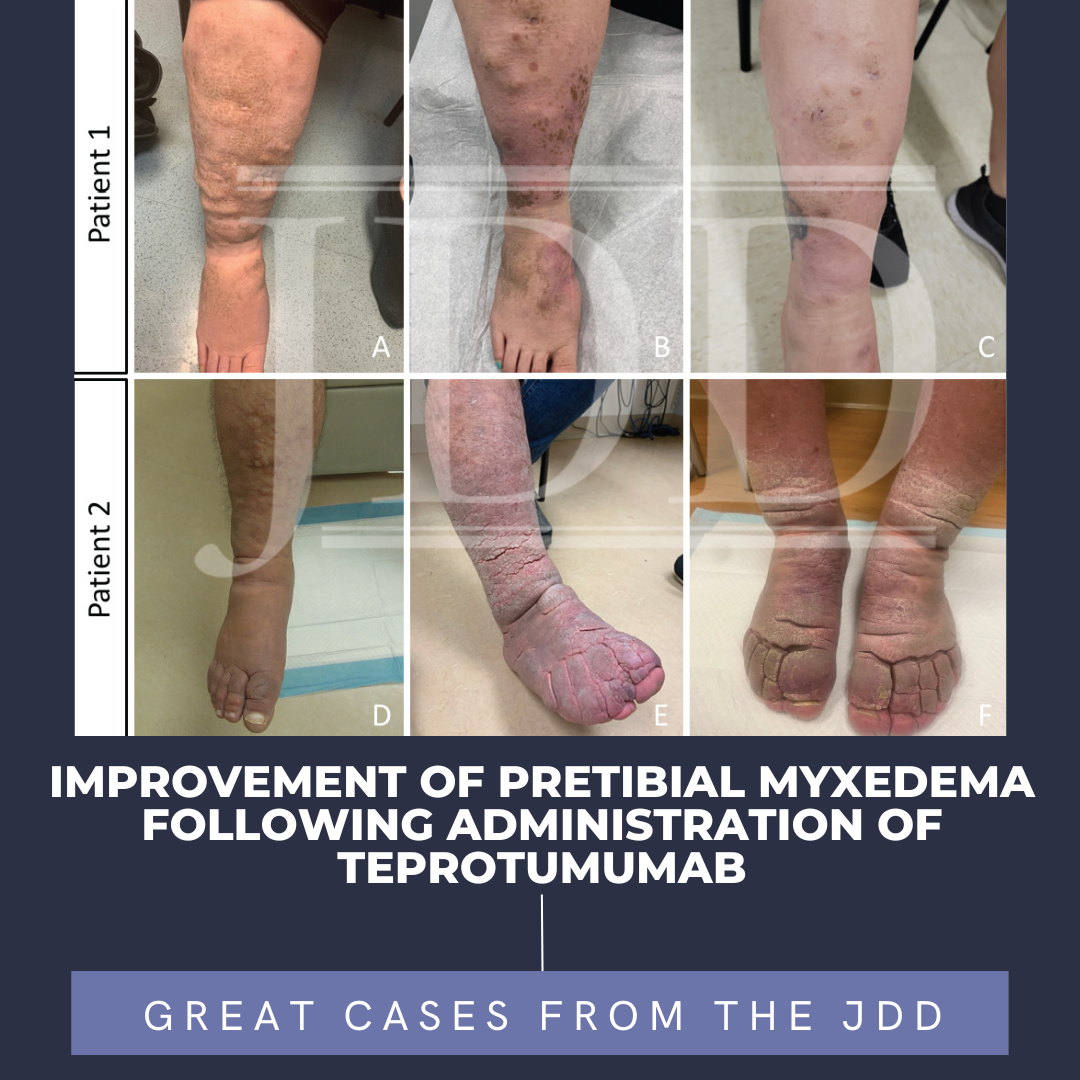 Pretibial myxedema (PTM) is a rare complication of Graves' disease. It is characterized by non-pitting edema with hyperpigmented hyperkeratotic papules and plaques on bilateral lower legs. Effective treatments for patients with PTM are lacking. The etiology of PTM is unknown; however, it may be similar to the mechanism of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO). Activated fibroblasts produce infla …
Pretibial myxedema (PTM) is a rare complication of Graves' disease. It is characterized by non-pitting edema with hyperpigmented hyperkeratotic papules and plaques on bilateral lower legs. Effective treatments for patients with PTM are lacking. The etiology of PTM is unknown; however, it may be similar to the mechanism of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO). Activated fibroblasts produce infla …  JDD authors Mihir Shah MD, Jenna Wald MD, and C. William Hanke MD MPH present a case of a patient with eruptive squamous cell carcinomas following treatment with Fludarabine to highlight not only the risk of cSCC in CLL patients and the increased risk for atypical cutaneous malignancies after treatment with systemic therapies such as fludarabine, but also to discuss treatment options for this …
JDD authors Mihir Shah MD, Jenna Wald MD, and C. William Hanke MD MPH present a case of a patient with eruptive squamous cell carcinomas following treatment with Fludarabine to highlight not only the risk of cSCC in CLL patients and the increased risk for atypical cutaneous malignancies after treatment with systemic therapies such as fludarabine, but also to discuss treatment options for this …  At ODAC 2023, we had the opportunity to learn about the latest in treatments for blistering diseases from Dr. Karl Saardi, Associate Professor and Director of Inpatient Dermatology at George Washington University. We focused on the pemphigus and pemphigoid group of diseases, which we will review and summarize here.
Pemphigus
The pemphigus group of diseases is characterized by intraepidermal auto …
At ODAC 2023, we had the opportunity to learn about the latest in treatments for blistering diseases from Dr. Karl Saardi, Associate Professor and Director of Inpatient Dermatology at George Washington University. We focused on the pemphigus and pemphigoid group of diseases, which we will review and summarize here.
Pemphigus
The pemphigus group of diseases is characterized by intraepidermal auto …