Evaluation of a Skin of Color Curriculum for Dermatology Residents
 Introduction
The term “skin of color” generally refers to individuals from a broad group of racial and ethnic backgrounds including, but not limited to, Black, Asian, Latinx, American Indian, and Pacific Islander, as well as those of mixed race.1 According to the U.S. Census, the population will increase to comprise over 50% persons of color by the year 2042.2 However, the demographics …
Introduction
The term “skin of color” generally refers to individuals from a broad group of racial and ethnic backgrounds including, but not limited to, Black, Asian, Latinx, American Indian, and Pacific Islander, as well as those of mixed race.1 According to the U.S. Census, the population will increase to comprise over 50% persons of color by the year 2042.2 However, the demographics …
 Introduction
The term “skin of color” generally refers to individuals from a broad group of racial and ethnic backgrounds including, but not limited to, Black, Asian, Latinx, American Indian, and Pacific Islander, as well as those of mixed race.1 According to the U.S. Census, the population will increase to comprise over 50% persons of color by the year 2042.2 However, the demographics …
Introduction
The term “skin of color” generally refers to individuals from a broad group of racial and ethnic backgrounds including, but not limited to, Black, Asian, Latinx, American Indian, and Pacific Islander, as well as those of mixed race.1 According to the U.S. Census, the population will increase to comprise over 50% persons of color by the year 2042.2 However, the demographics … Continue reading "Evaluation of a Skin of Color Curriculum for Dermatology Residents"


 With a special focus on patients with skin of color, the July issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology is packed with outstanding articles, features, and case reports on topics ranging from OTC therapies for hair grow and choosing the right sunscreen in communities of color, to evaluation of a skin of color curriculum for dermatology residents and PLLA for correction of nasolabial folds. Stra …
With a special focus on patients with skin of color, the July issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology is packed with outstanding articles, features, and case reports on topics ranging from OTC therapies for hair grow and choosing the right sunscreen in communities of color, to evaluation of a skin of color curriculum for dermatology residents and PLLA for correction of nasolabial folds. Stra … 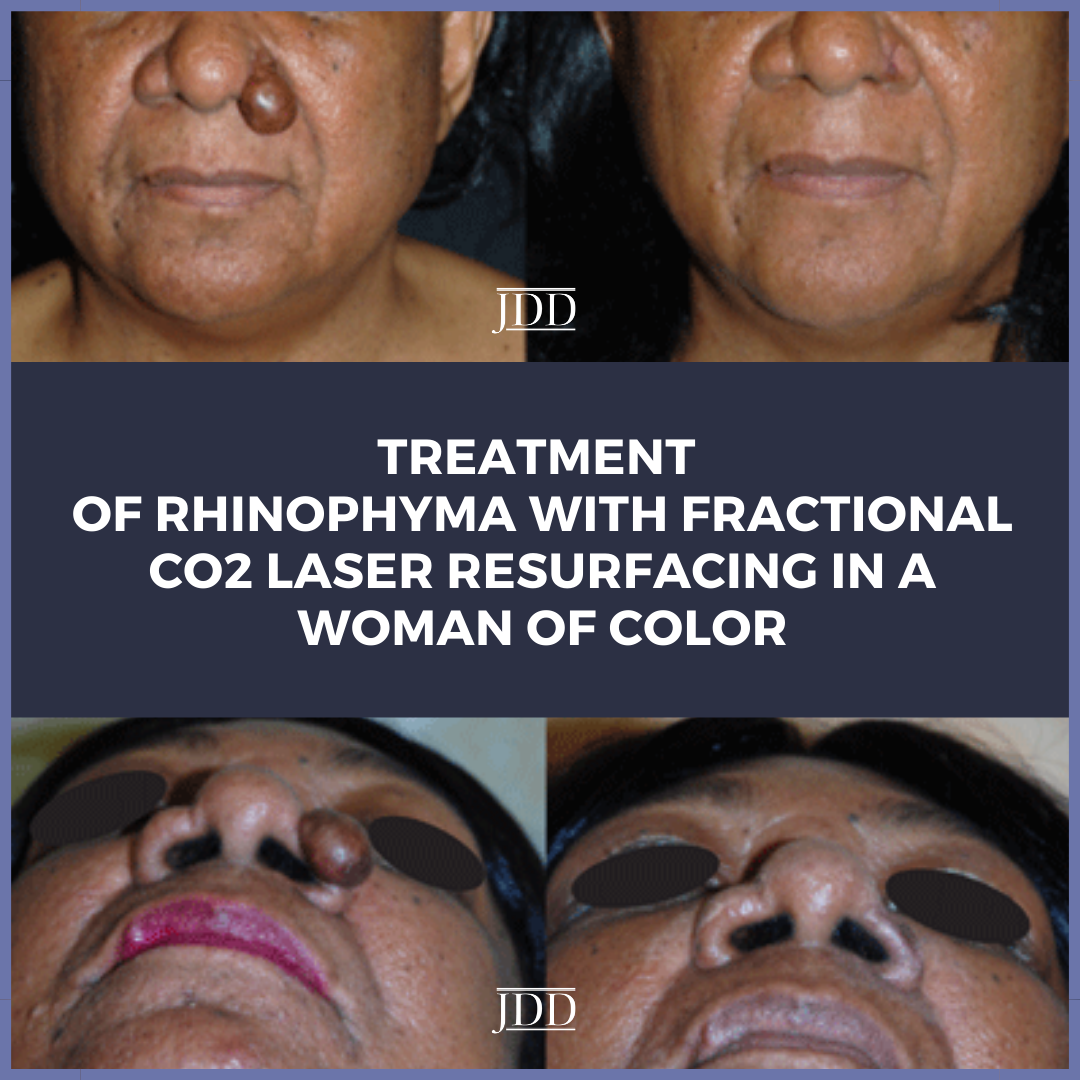 JDD authors Samuel S. Kassirer BA, Robert H. Gotkin MD, and Deborah S. Sarnoff MD present the first reported case of rhinophyma in a 62-year-old Fitzpatrick V female patient who was successfully treated with one session of fractional CO2 laser resurfacing. This case highlights the successful use of the fractional CO2 laser to treat rhinophyma in darker skin types (Fitzpatrick IV–VI) and undersco …
JDD authors Samuel S. Kassirer BA, Robert H. Gotkin MD, and Deborah S. Sarnoff MD present the first reported case of rhinophyma in a 62-year-old Fitzpatrick V female patient who was successfully treated with one session of fractional CO2 laser resurfacing. This case highlights the successful use of the fractional CO2 laser to treat rhinophyma in darker skin types (Fitzpatrick IV–VI) and undersco … 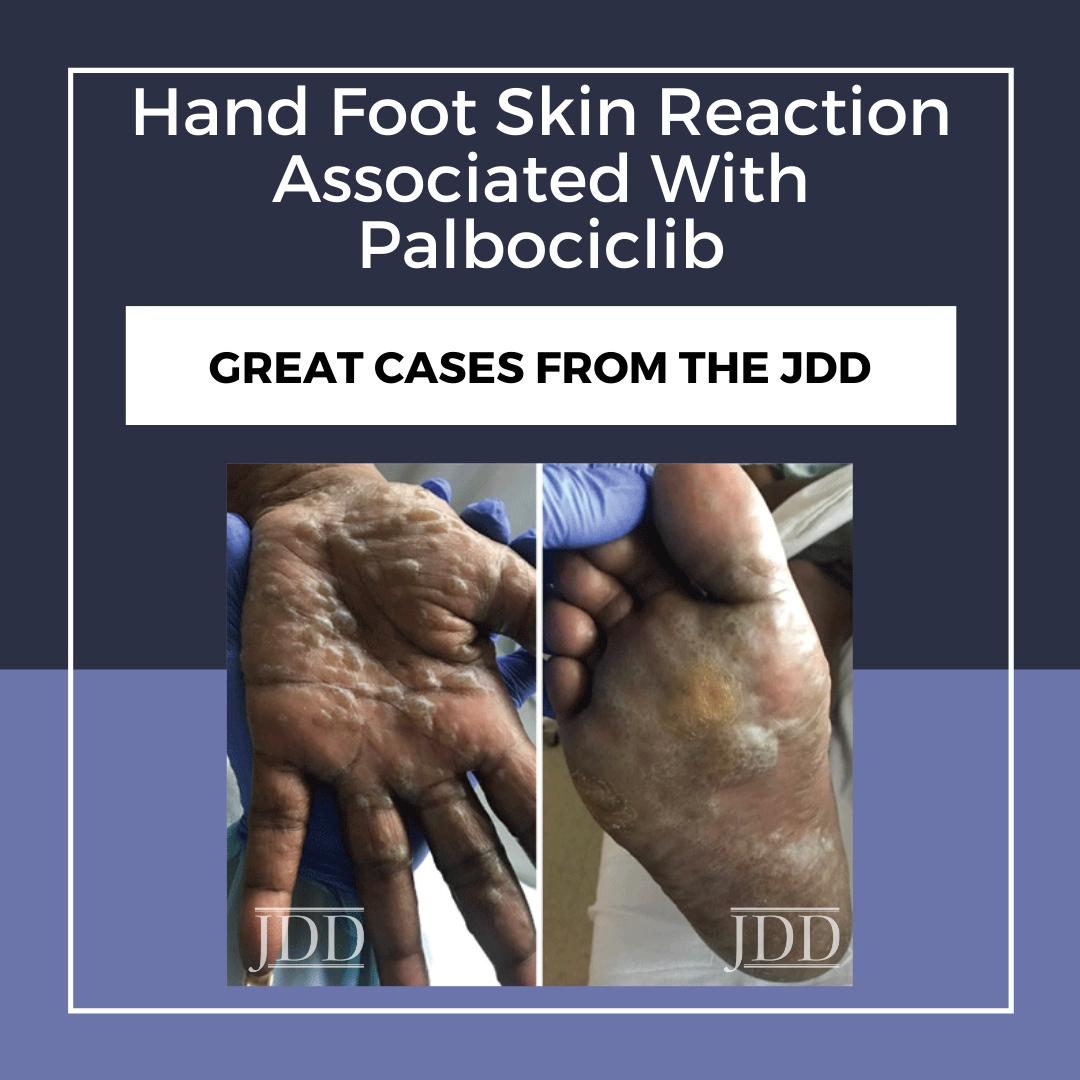 INTRODUCTION
Palbociclib is one of three new small-molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) approved for use in the treatment of hormone receptor positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative (Her2-) advanced or metastatic breast cancer. CDK4/6 inhibitors have a good overall safety profile but reported side effects include cytopenias, diarrhea, QTc pr …
INTRODUCTION
Palbociclib is one of three new small-molecule inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) approved for use in the treatment of hormone receptor positive (HR+) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative (Her2-) advanced or metastatic breast cancer. CDK4/6 inhibitors have a good overall safety profile but reported side effects include cytopenias, diarrhea, QTc pr …  The June issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology focuses on the topics of acne and rosacea, and features additional articles on topics such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Straight from the JDD Editor’s desk, we share this month’s issue highlights:
Guest Editor James Q. Del Rosso discusses roadblocks that impede patient ability to obtain medications selected by their dermatologist …
The June issue of the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology focuses on the topics of acne and rosacea, and features additional articles on topics such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Straight from the JDD Editor’s desk, we share this month’s issue highlights:
Guest Editor James Q. Del Rosso discusses roadblocks that impede patient ability to obtain medications selected by their dermatologist …