JAK Inhibitors in Pediatric Patients | Practical Pearls from the Expert
 Be excited about the new medications approved for use in pediatric patients, says Dr. A. Yasmine Kirkorian, chief of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital. Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference, interviewed Dr. Kirkorian about the use of JAK inhibitors in children. Should dermatology clinicians prescribe JAK inhibitors in this patient …
Be excited about the new medications approved for use in pediatric patients, says Dr. A. Yasmine Kirkorian, chief of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital. Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference, interviewed Dr. Kirkorian about the use of JAK inhibitors in children. Should dermatology clinicians prescribe JAK inhibitors in this patient …
 Be excited about the new medications approved for use in pediatric patients, says Dr. A. Yasmine Kirkorian, chief of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital. Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference, interviewed Dr. Kirkorian about the use of JAK inhibitors in children. Should dermatology clinicians prescribe JAK inhibitors in this patient …
Be excited about the new medications approved for use in pediatric patients, says Dr. A. Yasmine Kirkorian, chief of dermatology at Children’s National Hospital. Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference, interviewed Dr. Kirkorian about the use of JAK inhibitors in children. Should dermatology clinicians prescribe JAK inhibitors in this patient … Continue reading "JAK Inhibitors in Pediatric Patients | Practical Pearls from the Expert"


 Verywell Health and several other media outlets are covering the issue of melanoma overdiagnosis in light of a recent study, which estimated more than 80,000 melanomas were overdiagnosed in white Americans in 2018 alone. Is melanoma overdiagnosis among white Americans a significant issue? What are the driving factors of overdiagnosis? What can dermatologists do better when diagnosing melanoma? …
Verywell Health and several other media outlets are covering the issue of melanoma overdiagnosis in light of a recent study, which estimated more than 80,000 melanomas were overdiagnosed in white Americans in 2018 alone. Is melanoma overdiagnosis among white Americans a significant issue? What are the driving factors of overdiagnosis? What can dermatologists do better when diagnosing melanoma? … 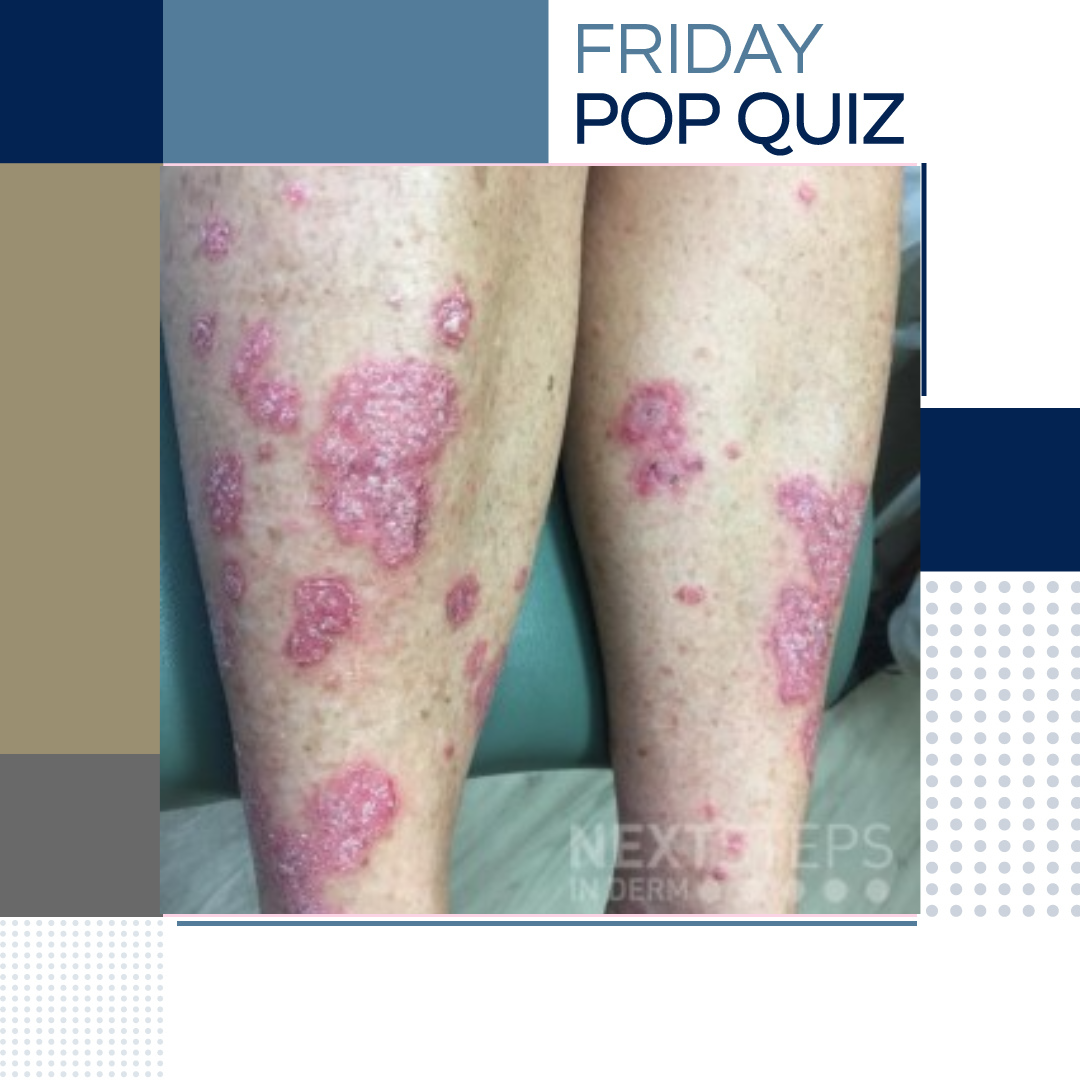 A 39-year-old woman presents for pruritic lesions of the bilateral lower extremities, as shown, without involvement elsewhere on the body. She denies joint pain, depressive symptoms, and difficulty with ambulation. She has previously tried treating the lesions with over-the-counter moisturizing cream without improvement. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the managemen …
A 39-year-old woman presents for pruritic lesions of the bilateral lower extremities, as shown, without involvement elsewhere on the body. She denies joint pain, depressive symptoms, and difficulty with ambulation. She has previously tried treating the lesions with over-the-counter moisturizing cream without improvement. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the managemen …  Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with Pigmentary Disorders Exchange Symposium interviewed Dr. Susan C. Taylor, Bernett L. Johnson Endowed Professor, director of the Skin of Color Research Fellowship and vice chair for diversity, equity and inclusion in the dermatology department at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Watch as Dr. Taylor shares the causes of photoda …
Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with Pigmentary Disorders Exchange Symposium interviewed Dr. Susan C. Taylor, Bernett L. Johnson Endowed Professor, director of the Skin of Color Research Fellowship and vice chair for diversity, equity and inclusion in the dermatology department at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Watch as Dr. Taylor shares the causes of photoda … 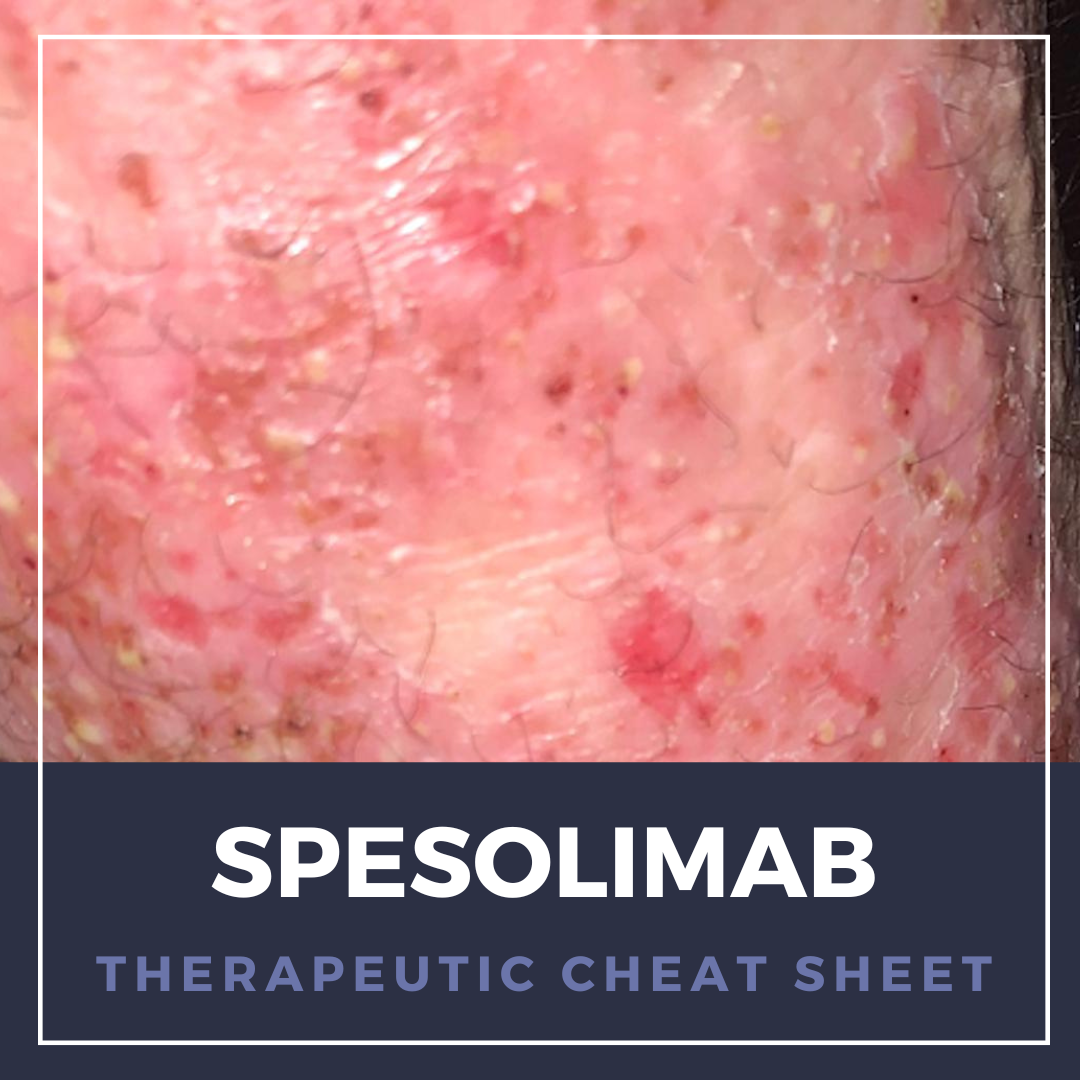 Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare, autoinflammatory condition, with acute, severe flares of diffuse sterile pustules and systemic symptoms that can be life-threatening. Historically, cyclosporine, methotrexate, retinoids, and biologics modulating the interleukin-17 (IL-17), IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor α pathways have been used off-label for management.1 Aberrant IL-36 signaling …
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare, autoinflammatory condition, with acute, severe flares of diffuse sterile pustules and systemic symptoms that can be life-threatening. Historically, cyclosporine, methotrexate, retinoids, and biologics modulating the interleukin-17 (IL-17), IL-23, and tumor necrosis factor α pathways have been used off-label for management.1 Aberrant IL-36 signaling …