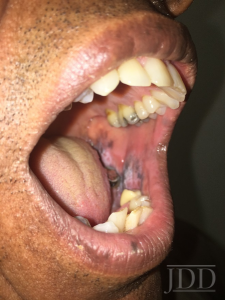
After starting multiple new medications in the past four months a 58 year-old man presented to clinic with a non-painful discoloration on his left buccal mucosa for the past three weeks. He also had a recent sinus infection treated with oral antibiotics. He denied tobacco use, alcohol use, and any dental work in the past three years. Biopsy showed focal hypergranulosis, necrotic keratinocytes, a jagged mucosal undersurface, and a lymphocytic infiltrate in the upper submucosa with scattered eosinophils and a few melanophages.
Which of the following medications is the most likely cause of the discoloration on his left buccal mucosa?
A. Amoxicillin/clavulanate
B. Azithromycin
C. Lorazepam
D. Lisinopril
E. Metformin
