A Massive Case of Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
 ABSTRACT
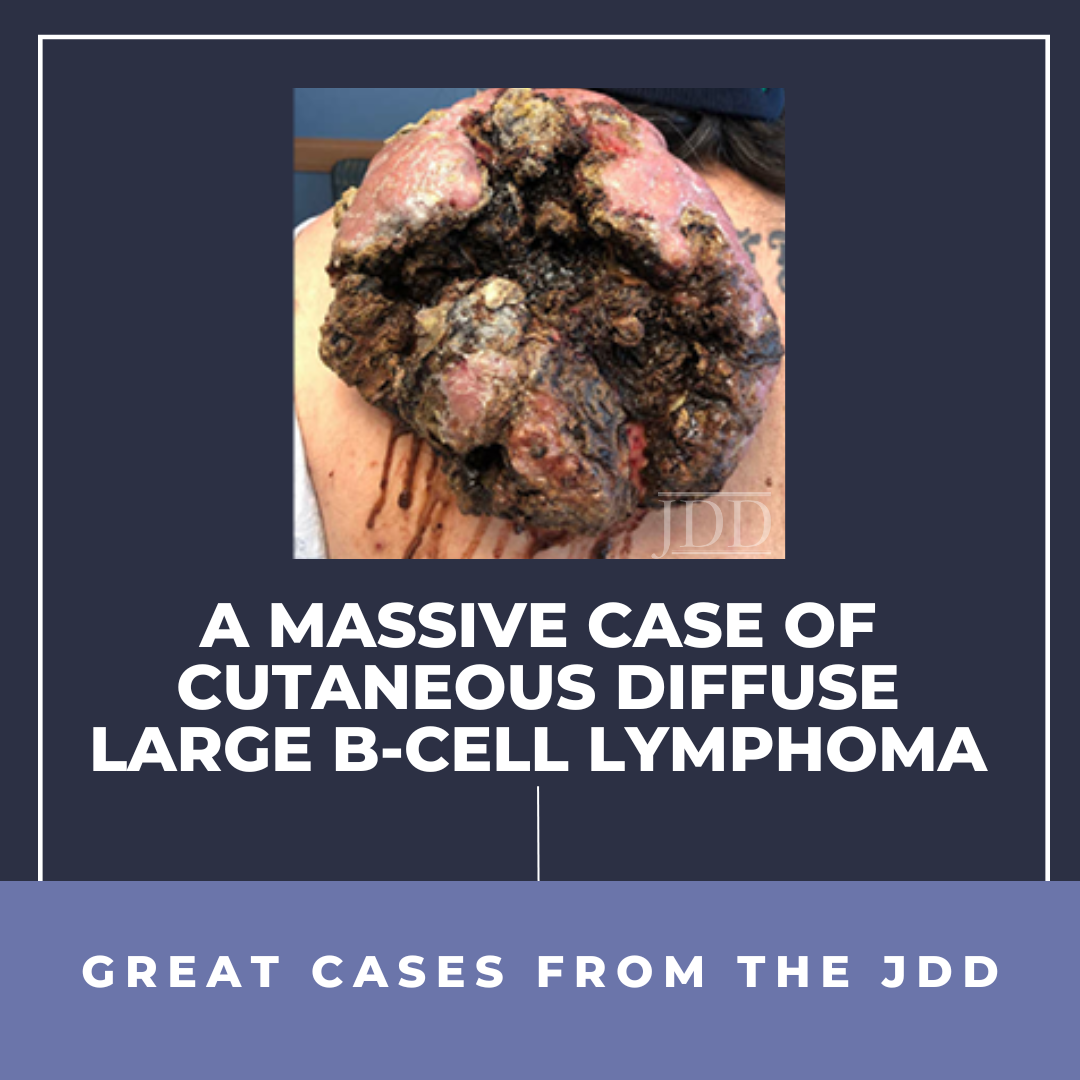
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and extranodal involvement is seen in approximately 40% of cases. However, cases involving the skin and muscle are rare, and skin manifestations most commonly present as plaques, papules, small nodules, or ulcers. In this report, JDD authors Lauren E. Merz MD MSc, Christopher B. Hergott MD PhD, and Reb …
ABSTRACT
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and extranodal involvement is seen in approximately 40% of cases. However, cases involving the skin and muscle are rare, and skin manifestations most commonly present as plaques, papules, small nodules, or ulcers. In this report, JDD authors Lauren E. Merz MD MSc, Christopher B. Hergott MD PhD, and Reb …
 ABSTRACT
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and extranodal involvement is seen in approximately 40% of cases. However, cases involving the skin and muscle are rare, and skin manifestations most commonly present as plaques, papules, small nodules, or ulcers. In this report, JDD authors Lauren E. Merz MD MSc, Christopher B. Hergott MD PhD, and Reb …
ABSTRACT
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and extranodal involvement is seen in approximately 40% of cases. However, cases involving the skin and muscle are rare, and skin manifestations most commonly present as plaques, papules, small nodules, or ulcers. In this report, JDD authors Lauren E. Merz MD MSc, Christopher B. Hergott MD PhD, and Reb … Continue reading "A Massive Case of Cutaneous Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma"


 Introducing the April 2024 Editorial Highlights from the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology! This month's issue is packed with groundbreaking research and insights into dermatologic treatments and practices. From original articles exploring innovative therapies for conditions like photoaging and acne vulgaris to case reports shedding light on rare dermatologic phenomena, this issue offers a comprehen …
Introducing the April 2024 Editorial Highlights from the Journal of Drugs in Dermatology! This month's issue is packed with groundbreaking research and insights into dermatologic treatments and practices. From original articles exploring innovative therapies for conditions like photoaging and acne vulgaris to case reports shedding light on rare dermatologic phenomena, this issue offers a comprehen … 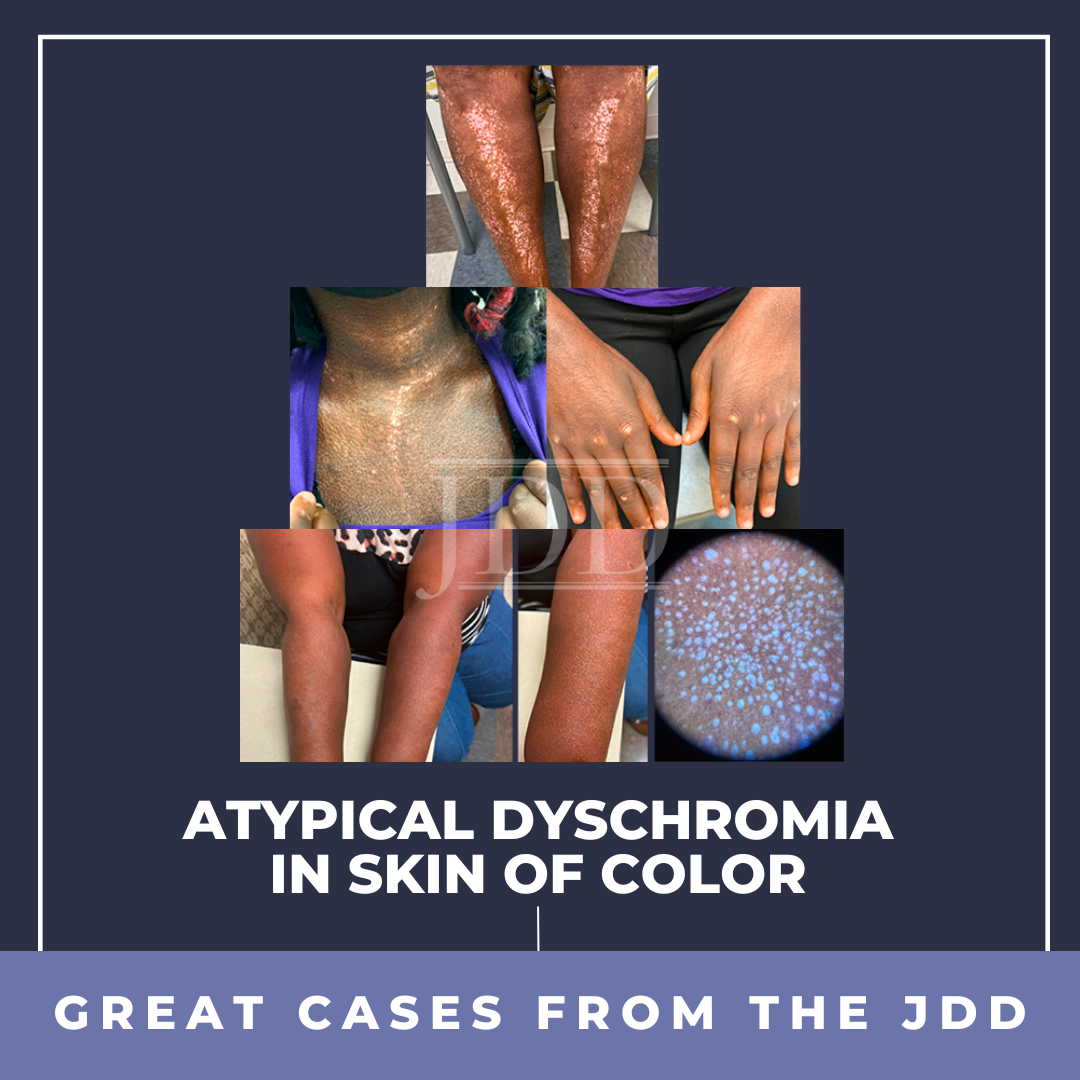 ABSTRACT
Dyschromia is a concern for many patients, especially persons of color. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation and depigmentation can affect all skin types; however, it is more apparent in those with darker skin. Some members of the dermatology community may not comprehensively understand the mechanisms of these reactions and the extent of the psychosocial effect they have on persons of color …
ABSTRACT
Dyschromia is a concern for many patients, especially persons of color. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation and depigmentation can affect all skin types; however, it is more apparent in those with darker skin. Some members of the dermatology community may not comprehensively understand the mechanisms of these reactions and the extent of the psychosocial effect they have on persons of color … 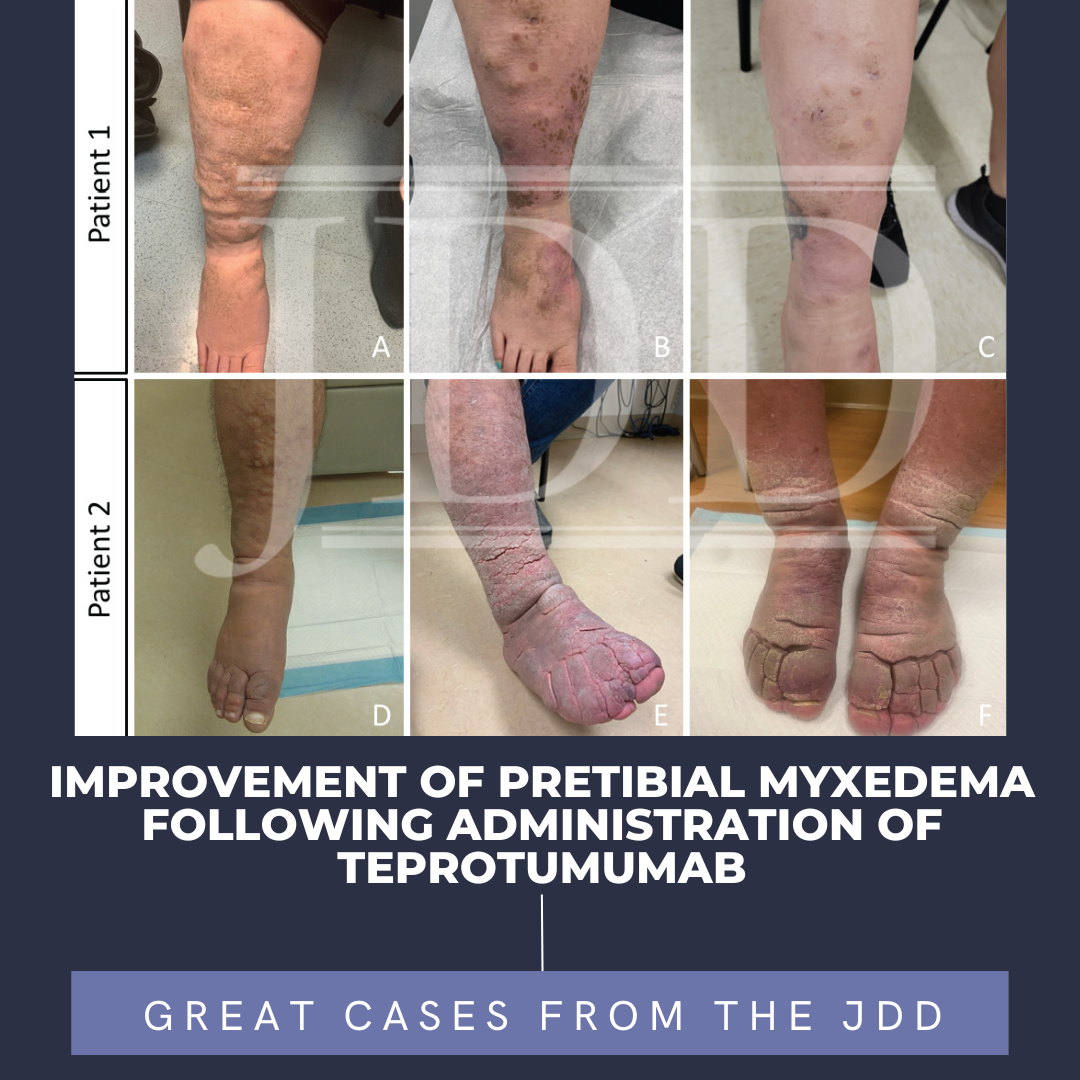 Pretibial myxedema (PTM) is a rare complication of Graves' disease. It is characterized by non-pitting edema with hyperpigmented hyperkeratotic papules and plaques on bilateral lower legs. Effective treatments for patients with PTM are lacking. The etiology of PTM is unknown; however, it may be similar to the mechanism of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO). Activated fibroblasts produce infla …
Pretibial myxedema (PTM) is a rare complication of Graves' disease. It is characterized by non-pitting edema with hyperpigmented hyperkeratotic papules and plaques on bilateral lower legs. Effective treatments for patients with PTM are lacking. The etiology of PTM is unknown; however, it may be similar to the mechanism of thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO). Activated fibroblasts produce infla … 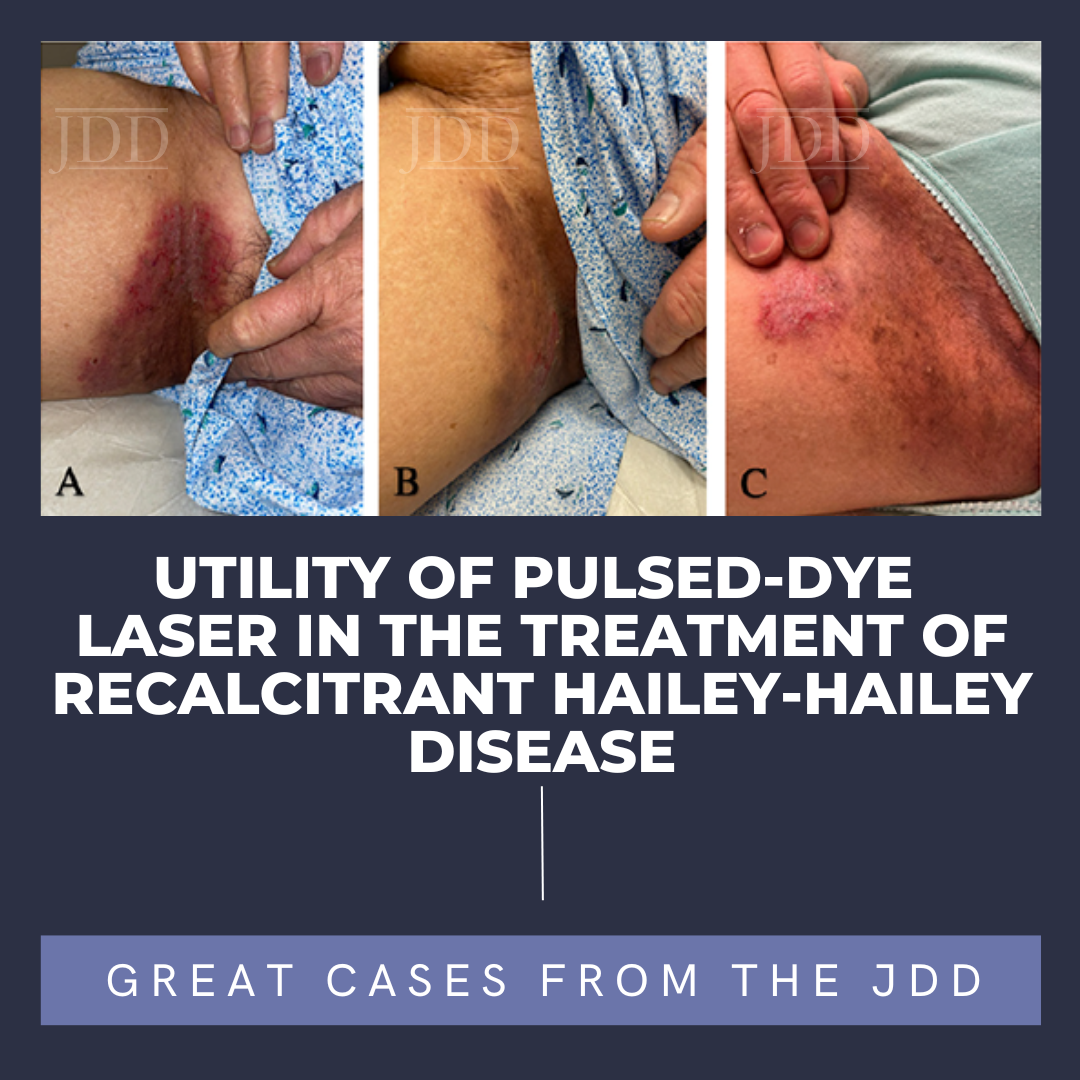 INTRODUCTION
Benign Familial Pemphigus, or Hailey-Hailey Disease (HHD), affects intertriginous areas of the skin causing epidermal blistering and vesicles that coalesce into weeping and crusting plaques.¹
The loss-of-function mutation of the ATP2C1 gene causes a disruption in calcium homeostasis of keratinocytes. The resulting dysfunction in desmosomes and cell-cell adhesion causes acanthol …
INTRODUCTION
Benign Familial Pemphigus, or Hailey-Hailey Disease (HHD), affects intertriginous areas of the skin causing epidermal blistering and vesicles that coalesce into weeping and crusting plaques.¹
The loss-of-function mutation of the ATP2C1 gene causes a disruption in calcium homeostasis of keratinocytes. The resulting dysfunction in desmosomes and cell-cell adhesion causes acanthol …