Friday Pop Quiz 9/6/2024
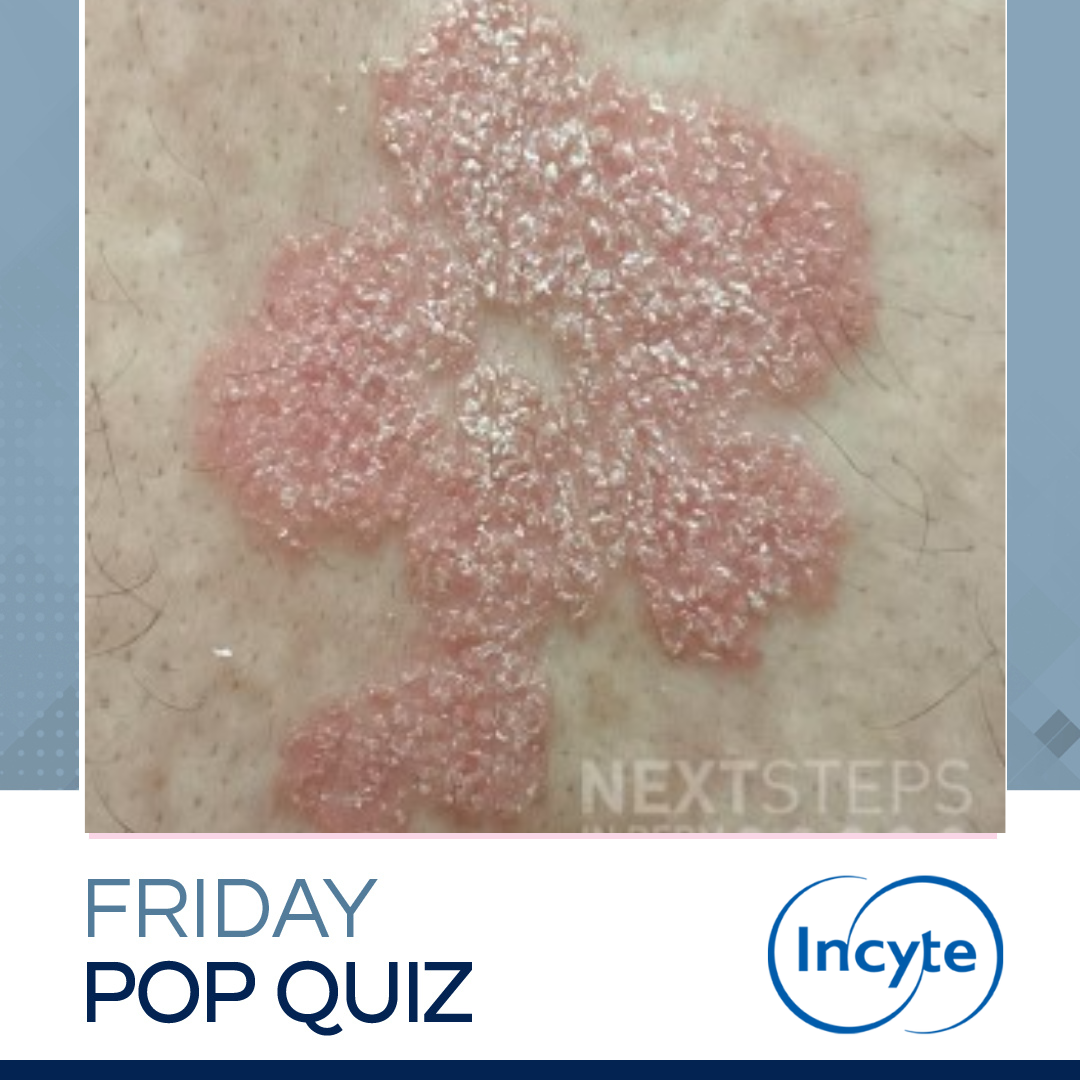 A 35-year-old woman presents to clinic with the skin lesions (shown) and joint pain. She was previously well controlled on guselkumab, but has flared since her dog was diagnosed with cancer. She has previously failed various treatments including topical steroids, methotrexate, narrow-band UVB, adalimumab, ixekizumab, and etanercept. She developed transaminitis and hepatic steatosis in response t …
A 35-year-old woman presents to clinic with the skin lesions (shown) and joint pain. She was previously well controlled on guselkumab, but has flared since her dog was diagnosed with cancer. She has previously failed various treatments including topical steroids, methotrexate, narrow-band UVB, adalimumab, ixekizumab, and etanercept. She developed transaminitis and hepatic steatosis in response t …
 A 35-year-old woman presents to clinic with the skin lesions (shown) and joint pain. She was previously well controlled on guselkumab, but has flared since her dog was diagnosed with cancer. She has previously failed various treatments including topical steroids, methotrexate, narrow-band UVB, adalimumab, ixekizumab, and etanercept. She developed transaminitis and hepatic steatosis in response t …
A 35-year-old woman presents to clinic with the skin lesions (shown) and joint pain. She was previously well controlled on guselkumab, but has flared since her dog was diagnosed with cancer. She has previously failed various treatments including topical steroids, methotrexate, narrow-band UVB, adalimumab, ixekizumab, and etanercept. She developed transaminitis and hepatic steatosis in response t … 

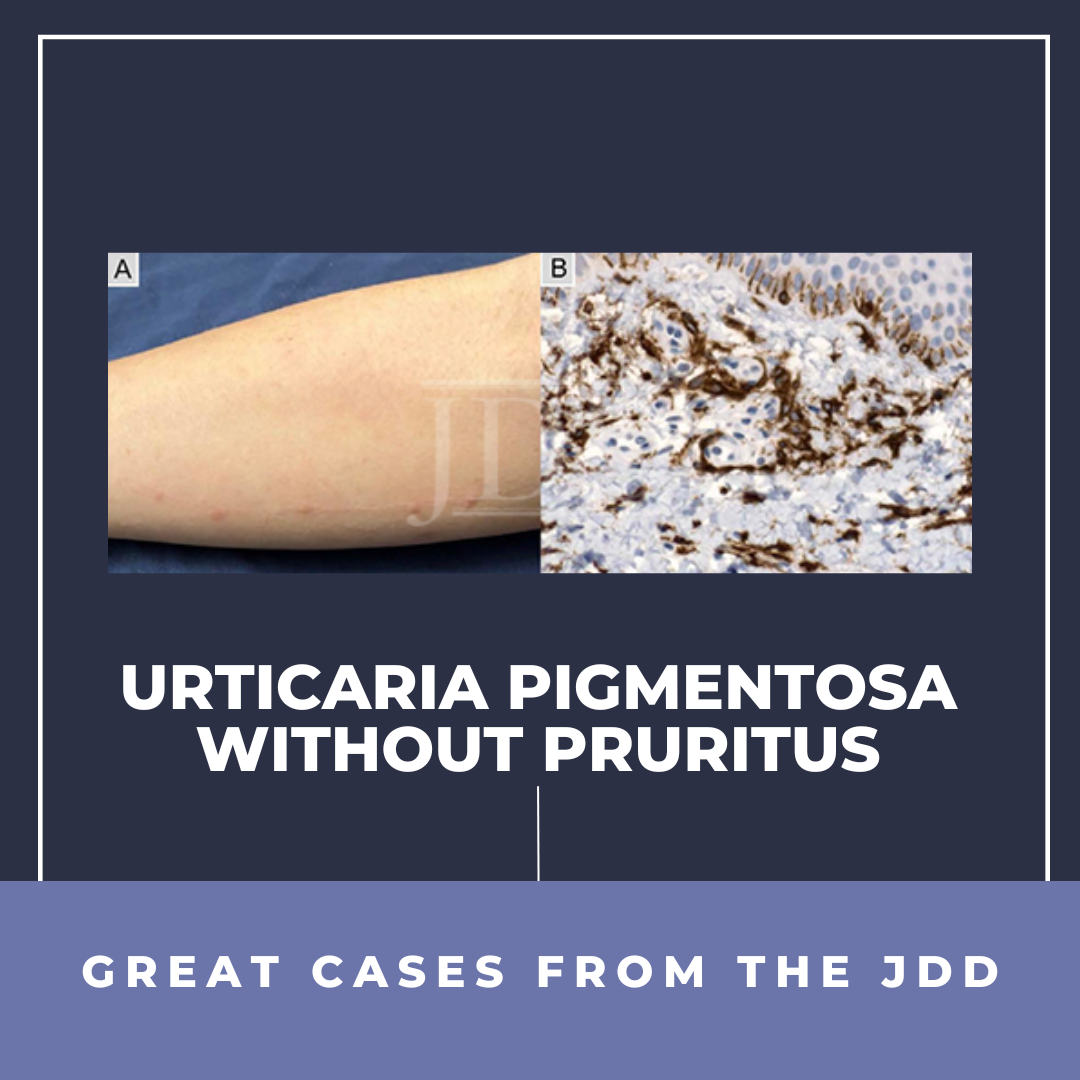 Mastocytosis is a group of disorders characterized by the pathologic accumulation of mast cells in various tissues. One example of mastocytosis is urticaria pigmentosa, which presents with mastocytomas that can cause hives and, when irritated, pruritus. To the authors' knowledge, they are describing the first case of urticaria pigmentosa without pruritus. The patient had a positive Darier' …
Mastocytosis is a group of disorders characterized by the pathologic accumulation of mast cells in various tissues. One example of mastocytosis is urticaria pigmentosa, which presents with mastocytomas that can cause hives and, when irritated, pruritus. To the authors' knowledge, they are describing the first case of urticaria pigmentosa without pruritus. The patient had a positive Darier' …  During the 2023 Skin of Color Update in New York City, esteemed experts, Dr. Andrew Alexis, Professor of Clinical Dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical College, and Dr. George Han, Associate Professor in the Department of Dermatology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, shared their expertise in diagnosing and managing psoriasis in individuals with skin of color …
During the 2023 Skin of Color Update in New York City, esteemed experts, Dr. Andrew Alexis, Professor of Clinical Dermatology at Weill Cornell Medical College, and Dr. George Han, Associate Professor in the Department of Dermatology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, shared their expertise in diagnosing and managing psoriasis in individuals with skin of color … 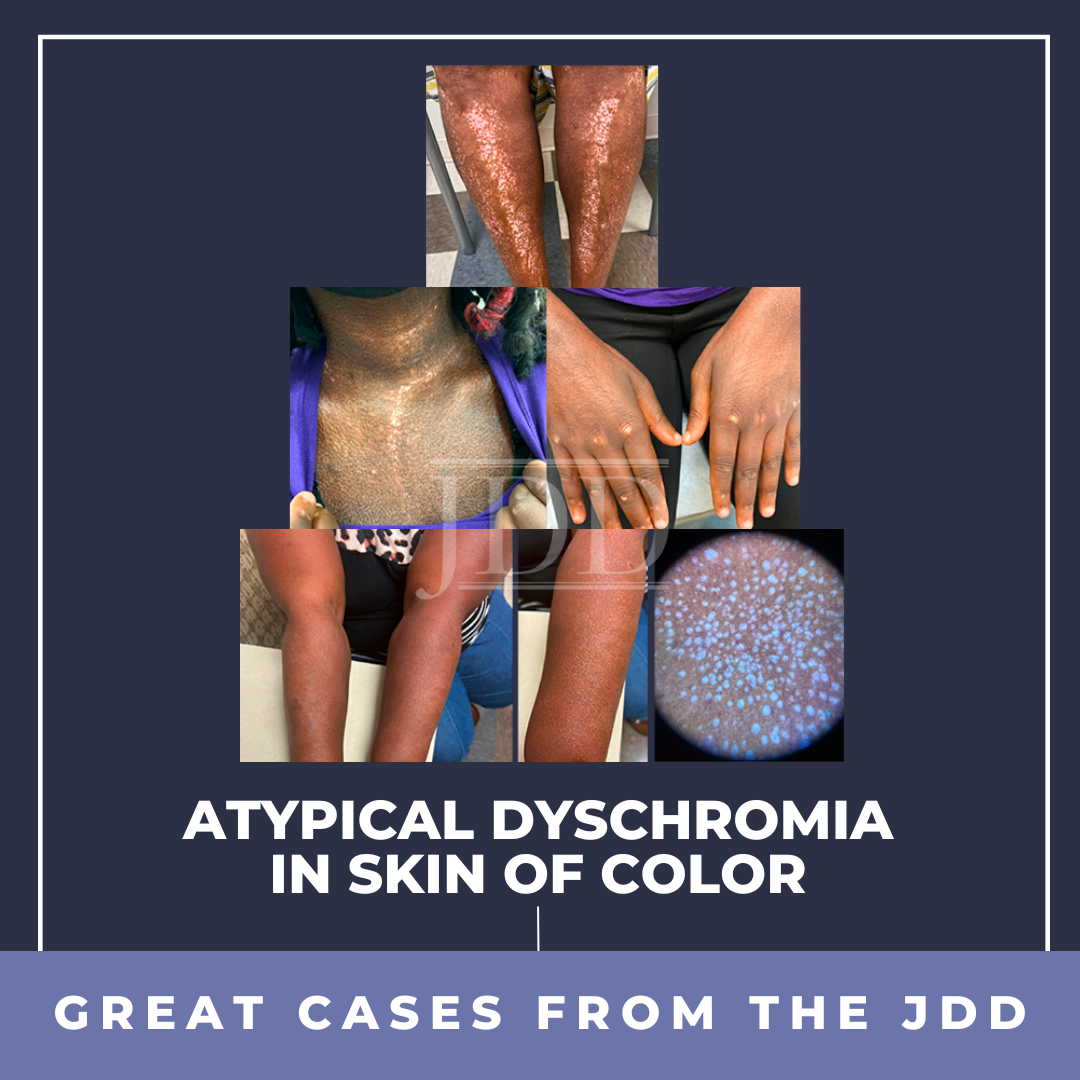 ABSTRACT
Dyschromia is a concern for many patients, especially persons of color. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation and depigmentation can affect all skin types; however, it is more apparent in those with darker skin. Some members of the dermatology community may not comprehensively understand the mechanisms of these reactions and the extent of the psychosocial effect they have on persons of color …
ABSTRACT
Dyschromia is a concern for many patients, especially persons of color. Postinflammatory hypopigmentation and depigmentation can affect all skin types; however, it is more apparent in those with darker skin. Some members of the dermatology community may not comprehensively understand the mechanisms of these reactions and the extent of the psychosocial effect they have on persons of color … 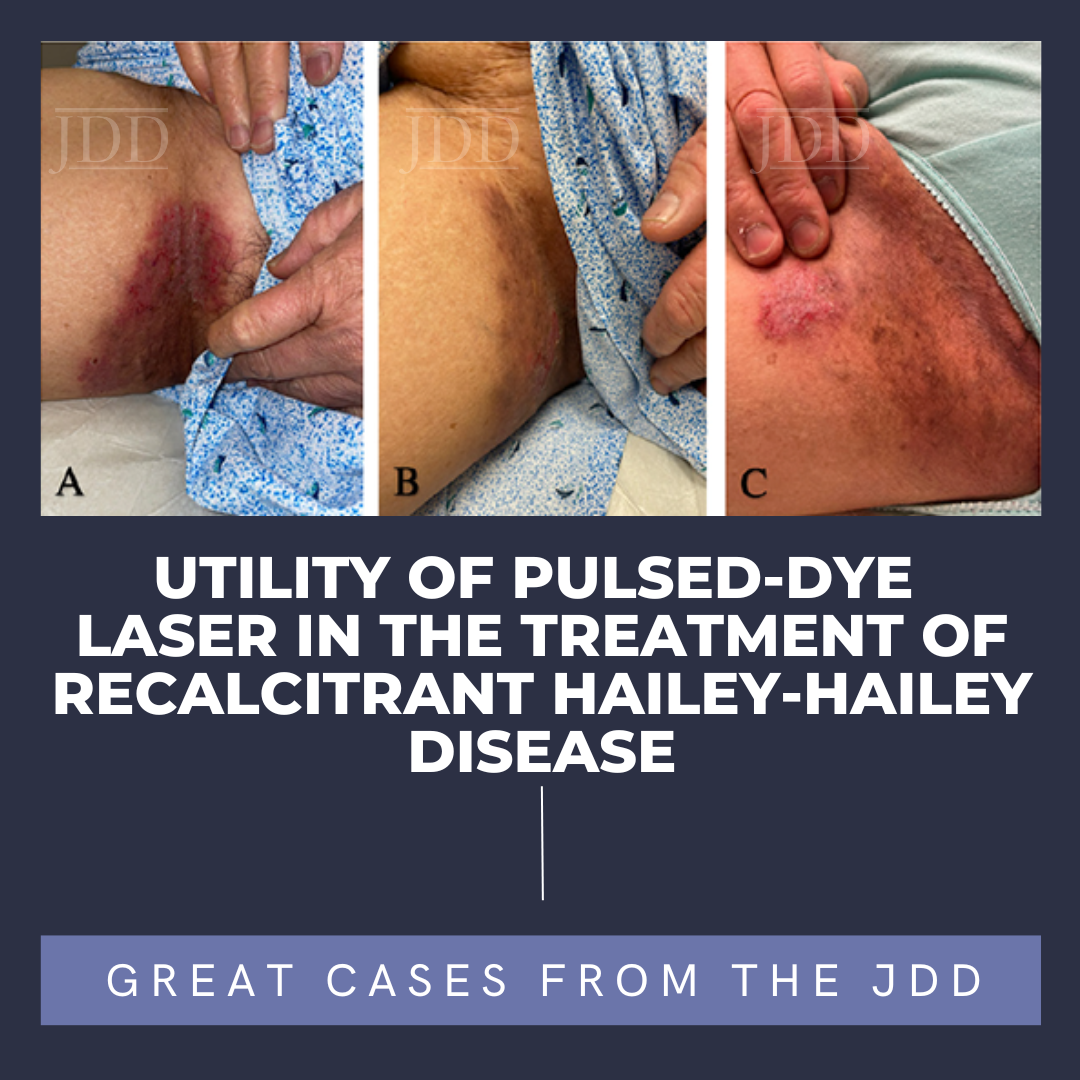 INTRODUCTION
Benign Familial Pemphigus, or Hailey-Hailey Disease (HHD), affects intertriginous areas of the skin causing epidermal blistering and vesicles that coalesce into weeping and crusting plaques.¹
The loss-of-function mutation of the ATP2C1 gene causes a disruption in calcium homeostasis of keratinocytes. The resulting dysfunction in desmosomes and cell-cell adhesion causes acanthol …
INTRODUCTION
Benign Familial Pemphigus, or Hailey-Hailey Disease (HHD), affects intertriginous areas of the skin causing epidermal blistering and vesicles that coalesce into weeping and crusting plaques.¹
The loss-of-function mutation of the ATP2C1 gene causes a disruption in calcium homeostasis of keratinocytes. The resulting dysfunction in desmosomes and cell-cell adhesion causes acanthol …