Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic skin condition characterized by pruritus, inflammation, and acute flare-ups of eczematous lesions over dry skin.1 The wide range of clinical manifestations, the visible nature of the disease, and the intense itching significantly affects patients’ quality of life.2 Up to 80% of children with AD experience sleep disturbances.3 Sixty-seven percent of children with AD are absent from school more than 1 day per year,4 and nearly 50% report a severely negative effect on their quality of life.5
Colloidal oatmeal is effective as an adjunct therapy in AD patients of all age groups, improving measures of disease severity such as Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA), Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI), pruritus, xerosis, and quality of life.6
Colloidal oatmeal cream is also effective as monotherapy for AD. In two studies, patients with mild-to-moderate AD treated with colloidal oatmeal 1% cream twice daily for two weeks experienced significant improvements in multiple disease severity indices.7 By day 3, 53.6 percent of subjects had a 20 percent improvement in EASI score, and 25 percent of subjects had a 20 percent improvement in Investigator’s Global Atopic Dermatitis Assessment (IGADA). In addition, 37.9 percent of patients experienced a 20 percent improvement in itch severity 10cm Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score immediately after application. The improvements in EASI, IGADA, and itch severity scores at other timepoints were also statistically significant. In the second study, patients’ assessment of itch severity significantly improved on days 1 (P=.0002), 7 (P<.0001), and 14 (P<.0001).7
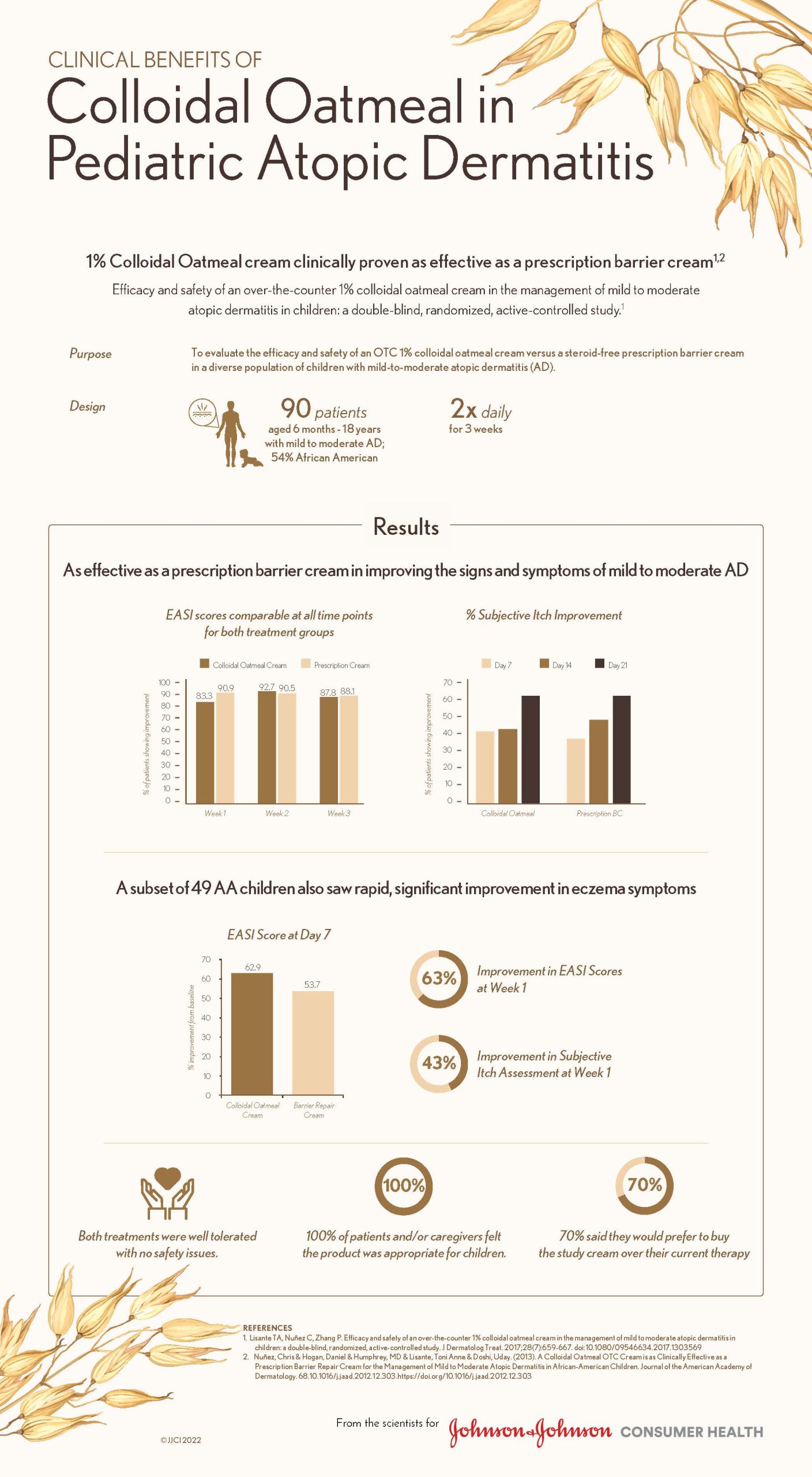
A recent double-blind, randomized, and active-controlled study showed that the effectiveness of colloidal oatmeal cream 1% was comparable to that of prescription barrier cream for treating mild-to-moderate AD in children.8 At week 3, changes in EASI scores of patients treated with oatmeal cream were “non-inferior” or comparable to those of patients treated with prescription cream. IGADA and VAS itch scores also improved in both treatment groups. Additional advantages of oatmeal cream are its ease of accessibility, as it can be purchased over-the-counter, and its low cost as compared to prescription barrier creams. Thus, oatmeal cream is a valuable alternative to prescription creams with promising treatment benefits.
Learn more by downloading the infographic below
References:
-
- Catherine Mack Correa M, Nebus J. Management of patients with atopic dermatitis: the role of emollient therapy. Dermatol Res Pract. 2012:836931.
- Watson W, Kapur S. Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2011; 7 Suppl 1:S4.
- Bawany F, Northcott CA, Beck LA, Pigeon WR. Sleep Disturbances and Atopic Dermatitis: Relationships, Methods for Assessment, and Therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 Apr;9(4):1488-1500. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.12.007. Epub 2020 Dec 13. PMID: 33321263; PMCID: PMC9026738.
- Eczema Prevalence, Quality of Life and Economic Impact (nationaleczema.org)
- Megha M. Tollefson, Anna L. Bruckner, SECTION ON DERMATOLOGY, Bernard A. Cohen, Richard Antaya, Anna Bruckner, Kim Horii, Nanette B. Silverberg, Teresa Wright; Atopic Dermatitis: Skin-Directed Management. PediatricsDecember 2014; 134 (6): e1735–e1744. 10.1542/peds.2014-2812
- Fowler JF, Nebus J, Wallo W, Eichenfield LF. Colloidal oatmeal formulations as adjunct treatments in atopic dermatitis. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11(7):804-807.
- Lisante TA, Nunez C, Zhang P, Mathes BM. A 1% Colloidal Oatmeal Cream Alone is Effective in Reducing Symptoms of Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis: Results from Two Clinical Studies. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16(7):671-676.
- Lisante TA, Nunez C, Zhang P. Efficacy and safety of an over-the-counter 1% colloidal oatmeal cream in the management of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children: a double-blind, randomized, active-controlled study. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017;28(7):659-667.
Did you enjoy this Skincare Monday post? You can find more on our OTC Resource Center.

